Part
01
of ten
Part
01
ESG Overview: Freddie Mac
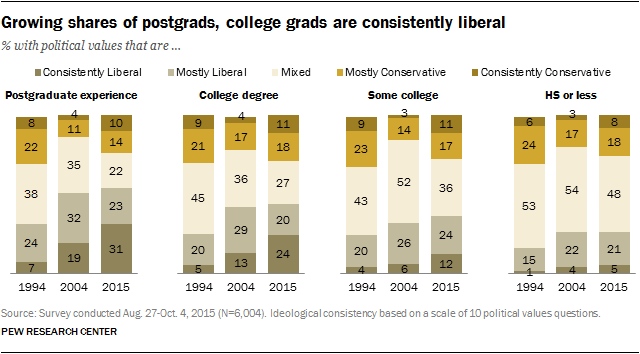
Freddie Mac relies on owned media in the form of its website, podcast, blogs, and Instagram account to communicate its ESG strategy (activities and initiatives). All the marketing communication methods are tailored to reach investors, ESG rating agencies, and other external audiences. The messaging, in some instances, is tailored to support the claims that are made surrounding ESG initiatives. More details can be found below.
About Freddie Mac
Freddie Mac is a company that provides affordable and accessible housing for ownership and renting. It operates in the secondary mortgage market. Its mission is to provide affordability, stability, and liquidity to America's housing market.
The Overall ESG Strategy (Initiatives and Activities)
- Freddie Mac's ESG strategy is well-defined and can be seen through the activities and initiatives that are undertaken on short and long-term basis.
Environmental:
- Green campus, and the Freddie Mac’s Green Advantage® program.
Social:
- Diversity and inclusion, comprehensive benefits, innovation, and a focus on community service.
Governance:
- Code of Conduct
- By-laws.
- Corporate governance guidelines.
- Committee charters.
- Investor relations.
- Leadership and management structure.
ESG Initiatives' Messaging and the Marketing Communications Strategy
Social
- Freddie Mac has a careers' blog where it posts details surrounding the commitment that it has to comprehensive benefits, innovation, the focus on community service, and diversity. The blog is dedicated to posting content about employee life, community activities, and other information that is helpful to the readers in their daily lives. For example, there is content about COVID-19, virtual internships, and working from home.
- The messaging attached to the blog is, "Freddie Mac is your destination employer because more happens here. Find out more about our commitment to diversity, comprehensive benefits, innovative culture and focus on community service."
- On the "Our People" page on the company's website, there is a lot of information surrounding the social criteria. From the people to the suppliers, there is a clear definition of the initiatives that are in place within the company.
- A good example is, "We emphasize diversity in our people because it’s smart business. Our focus on an inclusive workplace that values different perspectives makes us a stronger company, drives innovation, and supports our efforts to make home possible for America’s families. Our commitment to diversity starts with our hiring process, where we ensure all interested candidates are given a fair opportunity and consideration." This is the type of messaging that is directed to the general audience and focuses on the social criteria by touching on issues of inclusion.
- A separate segment on the website is dedicated to suppliers and includes information about how the company welcomes diverse suppliers and aims to ensure transparency and inclusion in the procurement of goods that support its business and operations. ESG communication is also seen through clear articulation that the suppliers are vetted for the promotion of human rights and other criteria.
- On its Instagram account, there are several posts that are dedicated to meeting the social criteria. This post focuses on the company's drive to build a diverse and inclusive culture and address any inequalities in the housing sector which it operates in.
- Freddie Mac also has a podcast that is dedicated to providing consumers and listeners with information and insights surrounding housing. However, there is clear marketing of ESG strategy and initiatives on the podcast called "Freddie Mac Single-Family Home Starts Here Podcast." This can be seen via episodes that discuss how the company is committed to the home buyers (Social criteria) and their desire to provide sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions (Environmental criteria). The podcast is free and can be accessed by investors, ESG rating agencies, and other external audiences. A multi-family podcast is also available.
Governance
- Information on initiatives surrounding corporate governance is openly displayed on the website within the Corporate Governance page. It can be accessed by all types of audiences including the investors and ESG rating agencies. Details include the code of conduct and the authority of the board. This also includes controls to the check the behavior and powers of the company's leadership. There are by-laws, corporate governance guidelines, and committee charters, which are all linked within the web page for easy access.
- The investor relations segment of the website can be used to access all the strategies and initiatives that the company has put in place to control the activities of shareholders.
- The messaging about governance is clearly articulated and geared towards showing that the company meets the necessary criteria. An example of messaging is, "Freddie Mac has built our business on the basis of service, trust and confidence, making us a leader in the mortgage finance industry. How we conduct ourselves, both individually and collectively, represents the conduct of Freddie Mac. Freddie Mac has had a strong Code of Conduct for many years, with separate versions that apply to employees and Directors."
- Details surrounding auditing are also displayed on the website with a chronological account of its activities and impact on the company's governance. The messaging is clear and conclusive about the initiatives that the company has put in place to achieve efficient governance. This can be seen through the following statement, "Freddie Mac's complaint policy for accounting, internal accounting controls and auditing matters pertaining to the company's business has been created in accordance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the corporate governance rules of the NYSE."
- The management structure is also displayed on the website from the CEO to the Senior Vice President, Chief Human Resources Officer and Chief Diversity Officer. Each leader has a full description attached to their profile, proving that they are qualified for the position. The management structure also supports the company's claim of supporting diversity and inclusion. The website provides access to the Board of Directors.
Environment
- The website is also used as a marketing communications strategy for the environmental initiatives.
- The Green Campus is discussed on the "Our Communities" website and it contains a brochure revealing the efforts that the company has put in place to ensure sustainability, recycling, and the reduction of GHG emissions.
- The messaging is stern and action-oriented, showing that the company's actions are supporting their claims. Freddie Mac states that they are working towards building earth-friendly, sustainable practices in every part of their business to minimize the impact that they have on the environment.
- Messaging that supports this claims and has been used as communication to investors, ESG rating agencies, and other audiences is then attached. Examples of wording used in the messaging are:
- "145 tons of organic food waste composted. That's the weight of 3 commercial jet airplanes."
- "2 electric car charging stations on campus. In just 8 months, our charging stations have saved 898 gallons of fuel from being used."
- There is a separate blog linked to the website that contains articles about environmental conservation and issues like green homes, green improvements, and eco-friendliness. The messaging in these articles is directed towards general audiences and it makes the company meet environmental and social criteria.
- On its news' web page, there are posts focused on discussing the community and environmental initiatives. For example, this release discusses an ESG initiative called "Freddie Mac's Green Advantage Program" that aims to attract investors.