Part
01
of one
Part
01
Written Communication in Business
Key Takeaways
- According to research by Website Planet, in the US, grammar errors in Google ads decrease traffic to a website by 5.2%, while spelling typos - by 10%. This translates into losing two customers for every 100 due to a grammar mistake, as well as four out of 100 due to a spelling mistake.
- A study by the National Association of Colleges and Employers found that 73.4% of employers want individuals with strong written communication skills.
- Across all company sizes and sectors, the global average of companies planning to invest in improving the English skills of their employees ranges from 3 — 4%.
Introduction
This research provides quantitative data points on the impact of written communication in business, including the impact of poorly written communication in business and the importance of written communication skills in business. Also, it presents quantitative data points on the use of English in global companies, whereby global companies are defined as those in or from countries where English is not the first language. Selected sources older than 24 months were used due to data limitations. The full explanation is provided in the Research Strategy section.
1. Impact of Written Communication in Business
Ads Containing Grammar or Spelling Mistakes
- In a poll by Survey Monkey, 81% of women and 77% of men consumers claimed they would not purchase a product or service advertised with poor grammar or misspelled words.
- Among young buyers, 85% of millennials noted that they are highly unlikely to purchase a product advertised with grammar or spelling mistakes. Additionally, 83% of people with annual household income of $75k or more said the same.
Further Data on Google Ads and Website Traffic
- According to research by Website Planet, in the US, grammar errors in Google ads decrease traffic to a website by 5.2%, while spelling typos - by 10%.
- This translates into losing two customers for every 100 due to a grammar mistake, as well as four out of 100 due to a spelling mistake.
- To compare, errors have an even higher impact both in the UK (traffic decreasing by 12.8% due to a grammar error and 14.1% due to a spelling error) and globally (declines of 8.7% and 13% for grammar and spelling mistakes, respectively).
Influencing Customer Perceptions
- Poor grammar, spelling mistakes, and typos affect a company’s reputation, thus, weakening its brand.
- A survey by Tidio revealed that 94% of U.S. consumers and 86% of global consumers are attentive to grammar. However, when shown sentences with poor grammar, only 2.8% of the respondents identified the mistakes.
- Overall, around 97% of the respondents claimed that grammar mistakes influence their perception of individuals (96.5%) and companies (97.2%).
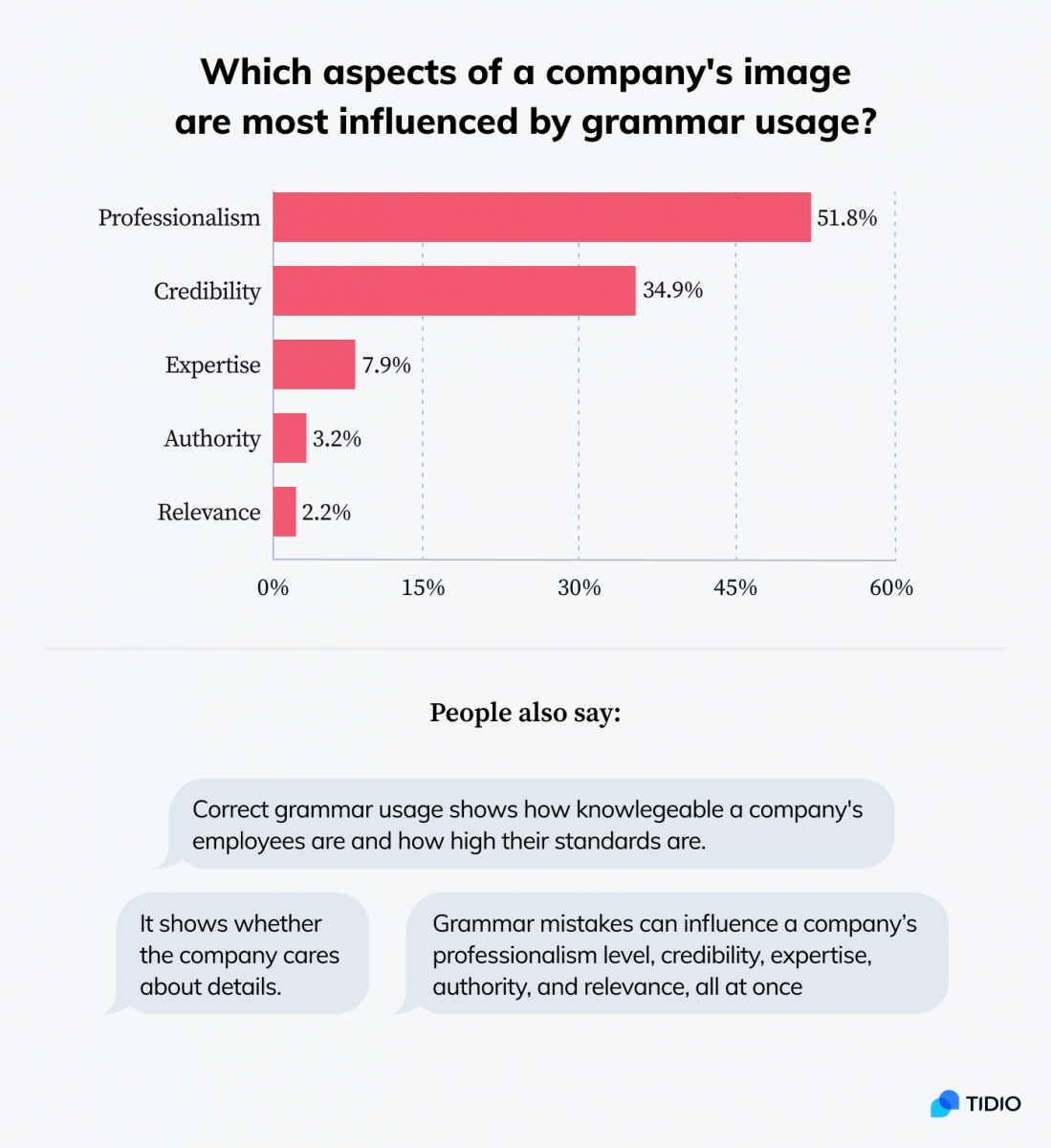
Impact on the Company Image
- Poor grammar erodes a company’s credibility.
- In a study, 51.8% of the respondents acknowledged that grammar influences how they perceive a company’s professionalism.
- Another 34.9% noted that grammar impacts how they view a company’s credibility. Thus, an estimated 96% of consumers use grammar to judge a company’s authority, eloquence, intelligence, and level of education.
Business Email Etiquette
- Nearly 75% of US workers believe that grammar and spelling mistakes are "a big deal" in business emails. However, the mistakes are considered forgivable if they don't distort the message.
- For additional context, the same survey by Rescue Time found that over 40% are against using emojis in business emails and under 20% are against using exclamation marks.
Time and Cost Savings
- Strong business writing skills are valuable, and individuals can enhance their value by more than 50% by honing their verbal and written communication skills, according to Warren Buffett, chief executive of Berkshire Hathaway.
- Good business writing skills save businesses time and cut costs. Employees and managers spend 22% of their time trying to make sense of a poorly written document or material.
- The time lost amounts to an estimated 6% loss in total wages, equivalent to about $400 billion yearly. Thus, poor writing skills cost organizations time and loss of wages.
Some of the Most Expensive Typos
- Some of the most expensive typos include:
- In 1962, NASA missed a hyphen when setting a trajectory and speed of Mariner 1, its first interplanetary probe. As a result, the spacecraft exploded minutes after the start. With the cost of $80 million, it was dubbed "the most expensive hyphen in history."
- In 1988, Banner Travel, a California-based travel agency, lost 80% of its business due to a typo in Yellow Pages ad, which changed "exotic" to "erotic." Given that the company mostly served seniors, the typo had a significant impact on its reputation. Pacific Bell, a company that published the ad with the typo, had to pay $10 million to Banner's owner.
- Lockheed Martin's deal for Hercules military transport aircraft considered "that the price of the planes would increase over time, to account for inflation." However, a formula calculating the increase had a misplaced comma, which costed the company $70 million.
Employers' Stance
- According to research, strong verbal and written communication skills are among the most sought-after by employers.
- Writing skills enable employees to communicate with colleagues, business partners, managers, third-party vendors, clients, internal department heads, etc. Poor writing skills can cause confusion and become costly in the long run.
- A study by the National Association of Colleges and Employers found that 73.4% of employers want individuals with strong written communication skills.
- Similarly, a poll by Survey Monkey found that 86% of hiring managers were less likely to hire applicants with grammar errors or typos in their job applications. The figure rose to 92% among those with at least $72k in annual income.
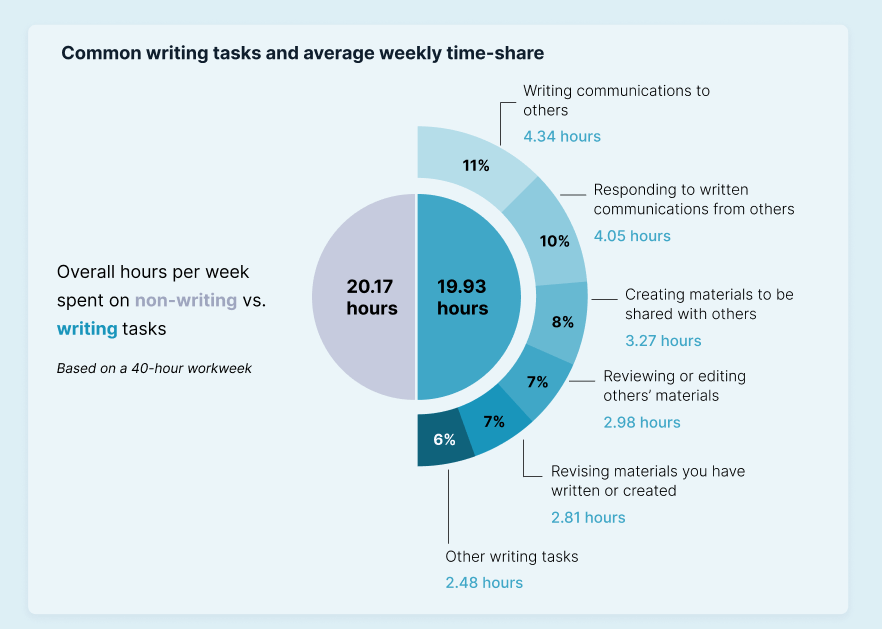
Share of Workplace Communication that is Written
- According to Grammarly, based on a 40-hour work week, about 20.17 hours are spent on non-writing communication, while 19.93 hours are spent on writing tasks.
- According to the report, 11% or 4.43 hours are spent writing communication to others, while 6% or 2.48 hours are spent writing other tasks.
- Employees are likely to spend "10% of their writing time or 4.05 hours responding to written communication from others, 8% or 3.27 hours creating materials to be shared with others, 7% or 2.98 hours reviewing or editing other's materials, and 7% or 2.81 hours are spent revising materials created or written."
The Importance of Email Communication
- Written, particularly email, communication in the workplace serves a wide range of purposes.
- According to research, email is commonly used in internal and team communications (74%) and client communication (70%).
- It is a preferred channel of business communication for 72% of millennials.
- Email is widely used when sharing work or projects internally (68%), sharing contracts (65%), important documentation (63%), and sharing project results with clients.
Importance of Written Communication for Leaders and Knowledge Workers
- According to Soocial, 86% of business leaders have communications budgets, with 68% planning to invest more in tools for written communication.
- 73% of knowledge workers feel confident about their written communication skills, but only 62% of them are perceived to communicate effectively.
- Furthermore, 54% of knowledge workers and 79% of business leaders experience written miscommunication, with up to 19% of workweek wasted due to poor communication.
Cost of Poor Communication - Additional Findings
- According to the State of Business Communication report 2022 by Grammarly, U.S. businesses lose about $1.2 trillion annually due to communication breakdowns.
- An estimated 9 out of 10 business executives have experienced the negative effects of poor communication at work.
- As per the report, poor communication increases the costs of business (45%), leads to missed deadlines/increased time to resolution (39%), erodes brand credibility or reputation (34%), and reduces productivity (28%).
2. The Use of English in Global Companies
Share of Employees With Sufficient English Skills
- According to English Assessment Cambridge, 49% of businesses in non-native English-speaking countries require employees with advanced levels of English.
- The global average of staff having English skills needed to succeed in their role includes 78% in top management, 74% in marketing, 64% in accounting and finance, 70% in sales, 60% in human resources or personnel, 65% in production, 68% in customer service, and 62% in logistics and distribution.
- According to the study, there is a gap between employees' skills and the skills each industry wants, translating to a global average of at least a 40% skill gap.
Level of English Required by Global Employers
- Global employers are looking for different levels of English proficiency when hiring for various positions. Notably, job descriptions will feature three typical levels of English, including business-level English, fluent English, and strong English communication skills.
- Depending on the nature of the task, 44% of global companies require advanced to native English level to write emails and participate in meetings, and 46% require it for delivering presentations and reading reports.
- However, some professions, such as banking, finance, and law, require the highest English proficiency levels than hospitality, leisure, and travel professions.
- Businesses in non-native English-speaking regions have the highest English-level requirements. More than 49% of such companies require advanced levels of English.
Percentage of Internet Businesses Using English
- According to Statista, data from W3Techs shows that about 63.7% of all websites use English for their content.
- Roughly 1.2 billion internet users speak English, about 25.9% of the world’s internet users. Thus, 3 in 4 people globally do not understand over 60% of all websites without a translation tool.
- The chart above shows the representation of language use across internet websites, whereby some languages, such as Russian, have a wider internet footprint than they are spoken globally.
Regions Investing in English
- Globally, many businesses, especially in non-English speaking regions, are investing in and attracting investments in English training.
- Recently, Telemia partnered with National Geographic Learning (NGL) to provide the Saudi Arabia Ministry of Education with learning materials to prepare about 150,000 Saudi students for the future labor market.
- EdTech startups, such as Englease.com, have raised funding to build an online English synchronous (live) education system for UAE clients. The company received seed funding of $3.4 million.
- In China, the world’s second-biggest economy, the English language training market is anticipated to grow by $80.54 billion during the 2021-2025 period at a CAGR of 22%.
Employers Planning to Improve the English Skills of their Staff
- Across all company sizes and sectors, the global average of companies planning to invest in improving the English skills of their employees ranges from 3 — 4%.
- The focus on improving English skills is mainly seen in top and middle management roles. As per the findings, 4% of global companies plan to improve the English skills of their employees.
- Another 4% plan to improve the English skills of their employees in accounting and finance, sales, human resources or personnel, customer services, and production. Another 3% plan to do so in marketing, logistics, and distribution.
- Despite the lower percentages, there is clear evidence that employers plan to improve the English skills of their employees across all job roles.
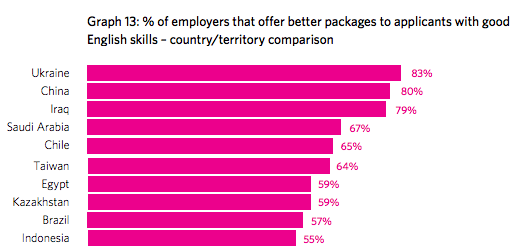
Countries Where Employers Reward English Skills
- Globally, around 50% of employers offer better packages to candidates with high English skills.
- In 2017, employers across various geographies rewarded applicants with good English skills with better offers. This included Ukraine (83% of employers), China (80%), Iraq (79%), Saudi Arabia (67%), and Chile (65%).
Research Strategy
For this research on written communication in business, we leveraged the most reputable sources of information available in the public domain, including reports and studies by Grammarly, Cambridge English, LinkedIn, Business Wire, PR Newswire, Inc, Statista, and Marketing Profs, among others. In some cases, we used sources older than 24 months. As previously noted, recent studies and surveys on the topic are limited. Hence, we used some slightly dated sources to add robustness to the report, after making sure that there aren't more recent findings on the topics covered.