Part
01
of one
Part
01
Startup Pivots
Key Takeaways
- The use of the word 'pivot' as a specific entrepreneurial term originates from entrepreneur and author Eric Ries' bestselling book 'The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Business.' He has defined pivot as being the "structural course of correction designed to test a new fundamental hypothesis." According to Eric Reis, there are ten different types of startup pivots.
- Customer segment pivot is a type of pivot that occurs when a product proves to be popular with a different customer segment than the one originally targeted. This pivot encourages companies to review and change their value proposition, product placement, pricing, and channels.
- Value capture pivot is a type of pivot that involves companies changing their monetization or product revenue model in order to capture value, mostly by charging customers money. Changing the revenue model "impacts the product, business, sales, marketing, and operational sides of the business model." A typical example includes software companies starting out by offering free versions of their product with minimal functionalities and later asking users to pay for the full version of the product.
- In a study conducted by Harvard Business Review Analytic Services, 71.6% of businesses surveyed claimed to understand the needs of its customers. However, only 35% of the customers interviewed in the same study felt that the companies truly understood their need. This indicates a sharp disparity in expectations between companies and their customers. In order to improve the quality of their products and services, companies can get customer feedback on their products or services through a number of ways, including emails, surveys, phone calls, focus groups, and digital channels. Companies can pivot by using the information gained regarding customer preferences through positive or negative customer feedback.
Introduction
The research brief provides insights on startup pivots, including the different types of pivots and factors that trigger pivots. The different pivots include zoom-in pivot, zoom-out pivot, customer segment pivot, customer need pivot, and value capture pivot, among others. Some factors that trigger pivots include customer feedback (positive and negative feedback), technology challenges, market conditions, and business financials, among others.
Insights on Startup Pivots
Different Types of Startup Pivots
- The use of the word 'pivot' as a specific entrepreneurial term originates from entrepreneur and author Eric Ries' bestselling book 'The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Business.' He has defined pivot as being the "structural course of correction designed to test a new fundamental hypothesis." The ten different types of startup pivots defined by Eric Ries are as follows:
- Zoom-in pivot: When a single feature in a product garners more interest and traction than the other features in that product, startups can pivot by offering a new product that contains only that specific feature. "This pivot helps organizations find and retain focus by delivering the minimum viable product (MVP) as fast as possible."
- Zoom-out pivot: This is the reverse of zoom-in pivot. In this type pf pivot, the product is broadened to include more features and eventually the whole product "becomes a single feature of a much larger product." Companies utilize this pivot when their research shows that the original product will not be able to support the customer needs and requires expansion.
- Customer segment pivot: This type of pivot occurs when a product proves to be popular with a different customer segment than the one originally targeted. This pivot encourages companies to review and change their value proposition, product placement, pricing, and channels.
- Customer need pivot: This type of pivot occurs when a company finds through early customer feedback that its product does not solve important problems of customers and is superfluous to their needs. "This pivot requires the product team to find a real customer problem worth solving and worth paying for."
- Platform pivot: This pivot involves companies changing "from an application to a platform or vice versa" since most customers purchase solutions and not platforms and product designers have to create their solutions keeping future products in mind.
- Business architecture pivot: According to Geoffrey Moore, author of the book 'Crossing the Chasm,' there are essentially two major business architectures, namely 'high margin, low volume (complex systems model)' and 'low margin, high volume (volume operations model).' While companies cannot have both architectures simultaneously, they can pivot from one architecture to the other from time to time.
- Value capture pivot: This pivot involves companies changing their monetization or product revenue model in order to capture value, mostly by charging customers money. Changing the revenue model "impacts the product, business, sales, marketing, and operational sides of the business model." A typical example includes software companies starting out by offering free versions of their product with minimal functionalities and later asking users to pay for the full version of the product.
- Engine of growth pivot: Startups have three primary growth engines, namely "viral (users promoting the product), sticky (customer retention), and paid growth models (advertising)." The engine of growth pivot involves startups pivoting from one growth engine to another.
- Channel pivot: Companies can deliver their products or services to customers through channels like in-store, online, in-app, or through partners. Channel pivot involves companies pivoting from one product delivery channel with lower sales effectiveness to another channel with higher sales effectiveness. This pivot often involves making adjustments to their product pricing, features, and\or competitive positioning.
- Technology pivot: This pivot involves companies using a different technology from their often-used technology to deliver solutions to their customers. "Companies make this pivot when new technology can provide superior price and\or performance to improve competitive position."
- Other types of pivots have also been defined by other authors and industry experts. These are as follows:
- Market segment pivot: This pivot occurs when a "customer pivot problem alters the functionality of a product while it is still sold in the same market segment." Since the product no longer serves the market it served earlier, companies have to sell the product in another market segment.
- Complete pivot: A complete pivot occurs when companies have to come up with a new idea for their product after the failure of their original idea/product. This pivot involves "significant change in one or more aspects of a startup, including product, targeted market, and finance."
- Side project pivot: Whenever a side product becomes more successful than the other main products of a company and eventually becomes the main focus of a company by overshadowing the other products, the pivot involves in the process is known as the side project pivot.
- Social pivot: This pivot involves a company changing its direction due to "active changes in social factors, such as persons and environments." However, this pivot is characterized by a considerable lack of scientific argumentation and supporting examples.
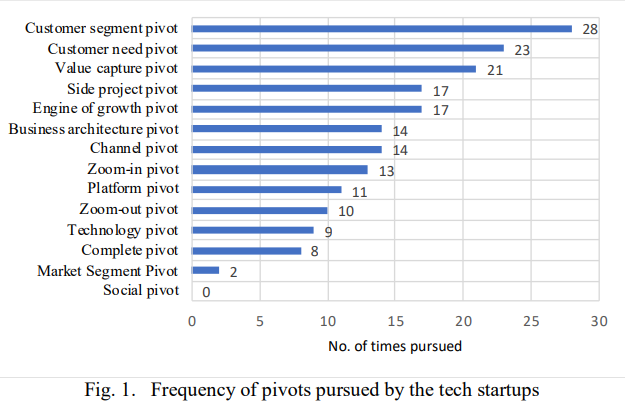
- In a 2021 study conducted by researchers from the London South Bank University, wherein secondary data from the pivots of 80 technology startups was collated, it was found that customer segment pivot (15%), customer need pivot (12%), and value capture pivot (11%) were the top-3 types of pivots by the tech startups. On the opposite end of the spectrum, social pivot (0%), market segment pivot (1%), and complete pivot (4%) were the least followed types of pivots. The other pivots types and their percentage frequencies were as follows: side project pivot (9%), engine of growth pivot (9%), business architecture pivot (7%), channel pivot (7%), zoom-in pivot (7%), platform pivot (6%), zoom-out pivot (5%), and technology pivot (5%).
Factors That Trigger Pivots
- Various academic articles and studies have identified the factors that trigger startup pivots. These factors are described below:
- Customer feedback (positive and negative feedback): In a study conducted by Harvard Business Review Analytic Services, 71.6% of businesses surveyed claimed to understand the needs of its customers. However, only 35% of the customers interviewed in the same study felt that the companies truly understood their need. This indicates a sharp disparity in expectations between companies and their customers. In order to improve the quality of their products and services, companies can get customer feedback on their products or services through a number of ways, including emails, surveys, phone calls, focus groups, and digital channels. Companies can pivot by using the information gained regarding customer preferences through positive or negative customer feedback.
- Technology challenges: When a company faces challenges with existing technologies and a new technology offers the company "superior price and\or performance to improve" its competitive position in the market, it generally pivots.
- Competition: Considering the immensely competitive nature of the startup space, startup companies pivot when they find that other companies in their space are absolutely dominating the market, capturing more customers, or are restricting them to a niche segment they are unhappy with.
- Unscalable business: A business becomes unscalable when it offers products or solutions that do not solve important problems of customers and are superfluous to their needs. In order to scale the business and remain competitive, the company needs to pivot, find real customer problems worth solving, and develop their products and solutions accordingly.
- Wrong timing: Sometimes a company may introduce a product or solution that the "market is not yet ready to accept." In such circumstances, the company will have to pivot in order to remain competitive in the market.
- Market conditions, including pandemics: Changing market conditions that include "shifting technological, regulatory, societal, cultural, and socioeconomic trends" and even pandemics can affect the viability of a company's business model, both at present and in the future. Such changing market conditions often trigger pivots among startup companies.
- Influence of investor, partner, or founder: Sometimes companies may face pressure or suggestions from their investors, founders, or partners to change their direction or value proposition. In such circumstances, startup companies generally pivot to reflect the changed direction or value proposition.
- Legal issues: Running into legal issues, such as legal problems with other companies or facing copyright claims from its competitors, may act as a trigger for startup companies to pivot.
- Flawed business model: Successful products, services, and technologies are supported and sustained by correct business models. If a company's business model is flawed, not even its value propositions or technologies/products/services that customers want can save the company from going bust. "The most obvious flaw is when a business model's value propositions generate more costs than revenues from customers. The business will inevitably disappear, even with the most successful value propositions." Hence, a flawed business model is an important factor for startup pivots.
- Side project success: Whenever a side product or service becomes more successful than the other main products/services of a company and overshadows them completely, the company feels the need to pivot and place more focus on that product/service for financial and business reasons.
- Business financials: Startup companies are often dictated by the financial state of their business and the amount of capital in the company. If the company is bleeding or running out of money, the founders will need to pivot to ideas or processes that make the company's operations more financially viable.
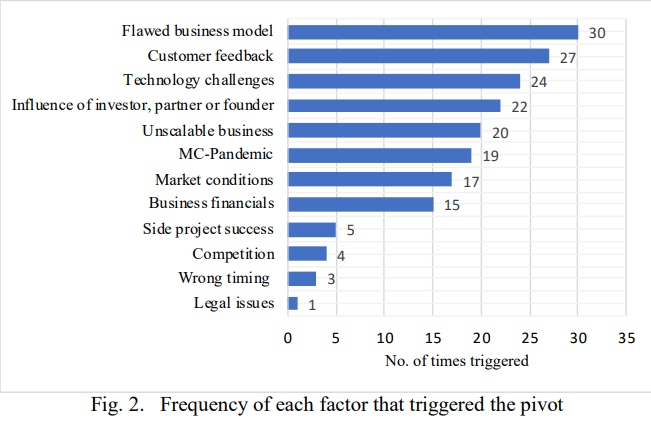
- In the aforementioned 2021 study conducted by researchers from the London South Bank University, wherein secondary data from the pivots of 80 technology startups was collated, it was found that the top-3 factors that triggered most pivots among startup companies were flawed business model (16%), customer feedback (14%), and technology challenges (13%). Conversely, legal issues (1%), wrong timing (2%), and competition (2%) were the factors that triggered the least number of pivots among startup companies. The other pivot triggering factors and their percentage frequencies were as follows: influence of investor, partner, or founder (12%), unscalable business (11%), pandemics (10%), other market conditions (9%), business financials (8%), and side project success (3%).
Research Strategy
For providing insights on startup pivots, including the different types of pivots and factors that trigger pivots, we have leveraged research reports and studies found on sources like ResearchGate and Springer LINK. We have also accessed articles and blogs by industry experts and reputable sources like HubSpot, OpenClassrooms, Applied Frameworks, and Strategyzer, among others. Some sources older than the Wonder standard of two years have also been included to provide robustness to the report.