Part
01
of one
Part
01
Potato Peel Extracts
Key Takeaways
- Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) is a technique used in the extraction of anthocyanins from potato peel using pure CO2 or CO2 with ethanol as a cosolvent.
- Pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) employs the use of conventional solvents at controlled pressures and temperatures. It yields more anthocyanin content as well as phenolic content compared with SFE using ethanol as a solvent.
- The major phenolic compounds extracted from potato peel using ultrasound-assisted extraction procedure with different solvents (methanol, ethanol, hexane, acetone, and water) were identified as chlorogenic acid(CGA), gallic acid (GAC), protocatechuic acid (PCA), and caffeic acid (CFA).
- Three major categories of polyphenols identified from potato peel extracts using sequential hydrothermal extraction (SeqHTE) technique are hydroxycinnamic acids (HCA’s), hydroxybenzoic acids (HBA’s), and flavonoids (flavanols, 3-hydroxyflavones, and flavanones).
Introduction
Insights on the extraction of high-value compounds from potato peel using four different extraction techniques are provided below. The techniques are supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), pressurized liquid extraction (PLE), ultrasound-assisted extraction, and sequential hydrothermal extraction (SeqHTE).
Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
- Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) is a technique used in the extraction of anthocyanins from potato peel. Anthocyanins are compounds with high antioxidant, anti-microbial, and antiproliferative activity. They are known for their nutraceutical value and health benefits. They are also used as food colorants because their color is pH-dependent.
- SFE is an efficient and environmentally friendly extraction technique for solid materials. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is typically used as the solvent due to its non-toxicity, relatively low critical temperature, non-flammability, good solvent power, low cost, and easy removal from the end product. However, the quantitative extraction of polar analytes like anthocyanins usually requires that an organic modifier be added.
- According to a research study, the percentage extraction yields obtained using pure CO2 and using CO2 + 5% (v/v) ethanol as a cosolvent are shown in the figure below. The addition of 5% (v/v) ethanol as a cosolvent to the CO2 provided the maximum extraction yields.
- The desirable conditions for the extraction of anthocyanin include low pressure (100 bar) and high temperature (65 °C).
Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
- Pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) employs the use of conventional solvents at controlled pressures and temperatures for the extraction of valuable compounds from natural sources. PLE technique requires less solvent and the extraction process is completed within a shorter time frame compared to extraction with traditional organic solvents.
- A key advantage of PLE over conventional solvent extraction techniques conducted at atmospheric pressure is that "pressurized solvents remain in the liquid state well above their boiling points, thus allowing high-temperature extractions. These conditions improve analyte solubilities and the desorption kinetics from the matrices".
- Using PLE the anthocyanin contents extracted are increased considerably compared with the corresponding SPE technique from the same research study above, and the optimum yields were obtained at 100 bar and 80°C. The solvent used was 80% (v/v) of ethanol in water acidified to a pH of 2.6 with acetic acid.
- The percentage extraction yields obtained using the PLE technique are shown in the figure below.
- Phenolic content can also be obtained using the PLE technique. The anthocyanin concentration (mg anthocyanins/mg dry extract) and phenolic total contents (mg phenolic total/mg dry extract) obtained with PLE are shown below. At 80 °C and 200 bar, the study found that the phenolic compounds are in a higher concentration than at 60 °C and 200 bar.
Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction
- Another research study used the ultrasound-assisted extraction procedure for potato peel extraction using different solvents; i.e. methanol, ethanol, hexane, acetone, and water.
- 20 ml of "solvent were added to 1 g of powdered peels, the mixture was sonicated in an ultrasonic bath for 15 min. The extract was filtered through Wathman No.42 filter paper for removal of peel particles and then centrifuged at 3000 × g for 10 min at 5°C and stored in a refrigerator".
- The major phenolic compounds extracted from the potato peel were identified as chlorogenic acid(CGA), gallic acid (GAC), protocatechuic acid (PCA), and caffeic acid (CFA).
- The tables below show the percentage yield of potato peel extract and total phenolic content obtained with the ultrasound technique from ground potato peels with the different solvents. The use of ultrasound improved the total phenolic compounds obtained from the potato peel extract.
Sequential Hydrothermal Extraction
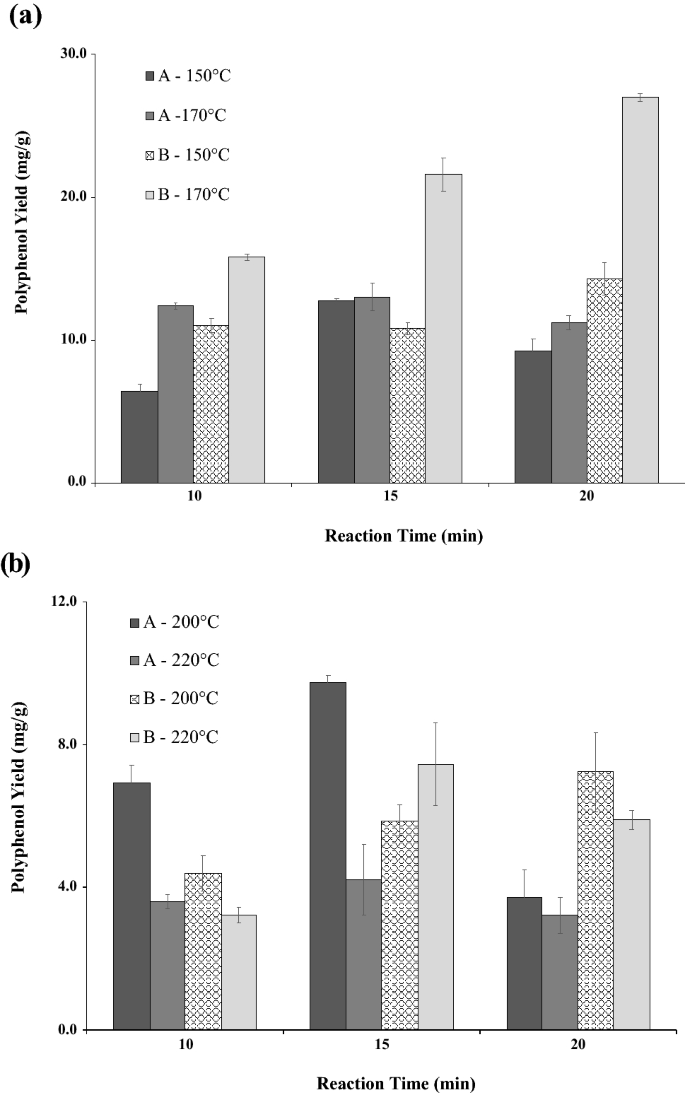
- A sequential hydrothermal extraction (SeqHTE) technique was employed by a third research study to extract high commercial value compounds from potato peels.
- Sequential hydrothermal extraction (SeqHTE) is a customized two-stage method that uses the unique characteristics of "subcritical water such as lower viscosity and interfacial surface tension to promote greater solvent penetration, enhance mass transfer, and breaking up the solid material into more soluble components".
- Two different samples were obtained from J. R. Simplot (Caldwell, ID), a Russet Burbank sample (sample A) with an 89 wt% moisture and another sample (sample B) consisting of a mixture of different peels with a 93.7 wt% moisture. The Russet Burbank sample had only dark brown skins; while the mixed sample had some yellow and brown colored peels.
- The highest extractions of polyphenols were 22.48 mg/g dry peel from the Russet Burbank sample and 32.87 mg/g dry peel from the mixture sample. The extracts showed significant antioxidant activities, measured as free radical inhibition, ranging from 40% to 92%. Glycoalkaloids, polysaccharides, and soluble nutrients were also extracted using the SeqHTE technique.
- Alkaloid extraction ranged "from 20 to 450 and from 35 to 610 mg/kg dry peel for the Russet Burbank and peel mixture, respectively. Similarly, polysaccharide yield varied from 0 to 35.7 wt%".
- Three major categories of polyphenols identified from the extracts are hydroxycinnamic acids (HCA’s), hydroxybenzoic acids (HBA’s), and flavonoids (flavanols, 3-hydroxyflavones, and flavanones).
- The figure below shows the polyphenol content of the extracts obtained with the SeqHTE technique on a dry peel basis.
Research Strategy
In the course of the search for insights on potato peel extraction, we found that detailed information can be obtained from academic research studies. We were able to provide insights on the extraction of high-value compounds using four different extraction methods from credible academic research sites such as ResearchGate, MDPI, and Springer.