Part
01
of one
Part
01
Future of Agriculture
Key Findings
- Precision Farming involves the application of agricultural technology (Ag-tech) in farming; from aerial imaging to the deployment of automated tractors and robots to soil sensors and a centralized management system.
- Vertical farming is often referred to as urban farming and involves (usually) indoor facilities to save space, time, and resources.
Introduction
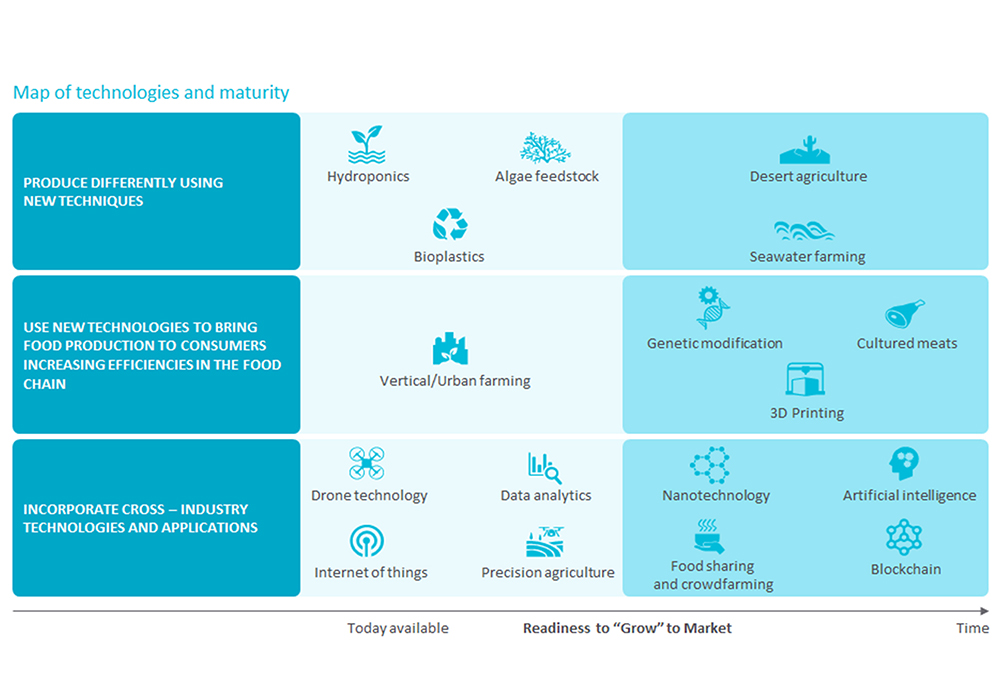
Emerging and future farming trends will provide greater yields and bigger crops as well as reduced waste and smaller carbon footprints. Among the most discussed trends in agriculture are precision farming and vertical farming. Additional trends include technology, regulations, and procedures that enhance agriculture's goal of improved sustainability. Complete details may be found in the attached presentation.
FUTURE AGRICULTURE TRENDS
Precision Farming
- The concept of precision farming, sometimes referred to as Ag4, involves incorporating field data, normally gathered by ag-technology hardware, and applying the data to field farming techniques, which frequently leads to lower uses of water, fertilizer, and pesticides, as well as improving crop yields. Precision farming helps to improve the environmental impact of farming.
- Data used in precision farming is collected via aerial imaging through the use of drones; soil sensors that collect environmental factors such as soil and plant moisture, soil acidity, organic material levels, and mineral levels present in the soil; and/or spectrometers used to detect plant stress and plant readiness. Once soil conditions are analyzed, farmers can utilize the correct type and quantities of seeds during planting processes through variable-rate seed technology; the control of how many seeds are applied for specific field locations.
- The end result of precision farming and a key factor in its increased implementation is improvements in sustainability leading to regenerative farming practices. As the globe realizes population increases, precision farming allows for increases in crop yields while lowering the use of limited natural resources.
Vertical Farming (Urban Farming)
- Acquiring better yields, less water usage, and better taste, vertical farming is an emerging trend in agriculture. "Plants grown with hydroponic methods don’t need extensive root systems, allowing them to devote more energy to the production of leaves and fruit. They also reach maturity faster and are safe from pests and diseases due to their indoor cultivation."
- Smaller footprints of vertical farms improve the industry's goal of improved sustainability. Aeroponics and hydroponics enhance growth of the plants in vertical farming. "Indoor vertical farms enable growers to control variables such as light, temperature, water, and sometimes, carbon dioxide levels, allowing them to get healthier and bigger yields."