Part
01
of one
Part
01
Supply Chains for International OEMs: Asia
Key Takeaways
- Denso Corp, Aisin Seiki, and Hyundai Mobis are top tier 1 suppliers in the Asian automotive industry. Yazaki Corp and BHAP are notable tier 2 suppliers in the industry. In recent years, labor rights violations have been reduced to a near insignificant level in the automotive supply chain, with the last reported violation in the industry occurring in 2019.
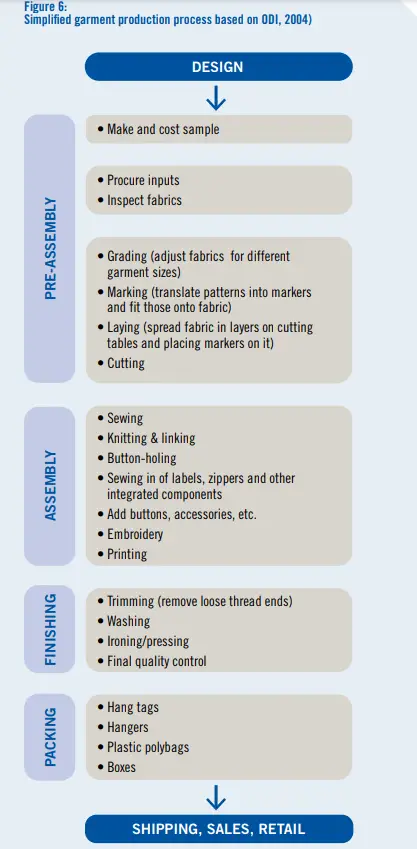
- The apparel supply chain in Asia is severely fragmented and mainly consists of local small and medium-sized businesses. Notable tier 1 suppliers in the industry include Golden Star, Karooni Knit Composite, and Interloop Limited. Pockets of labor rights violations still exist in the industry, with the latest major incident as recent as 2020.
- The top tier 1 suppliers in the Asian consumer electronics supply chain include Foxconn, Pegatron, and Wistron. Labor rights violations and protests are common occurrences in the Asian consumer electronics industry. All three tier 1 suppliers have been involved in labor rights violation incidences in the last two years.
Introduction
Details regarding the number of suppliers in each industry and examples of tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers in the supply chains of the automotive, apparel, and consumer electronics industries have been provided in this report. In addition, the number of employees at each supplier and recent labor rights issues and violations related to each supplier have been presented in this report.
AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY
Number of Suppliers
- There are currently no publicly available reports on the number of tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers that serve the Asian automotive industry. Attempts to locate this information proved abortive as the number of tier 1 or tier 2 automotive suppliers in the region has neither been determined nor publicly disclosed by independent bodies. However, the Asian automotive industry is presently the largest market for motor vehicles globally.
- The Asian automotive industry produces about 52 million motor vehicles per year, representing about 55% of total global production. In 2017, the automotive industries in China, Japan, India, South Korea, Indonesia, and Vietnam together provided 7.8 million jobs.
Main Suppliers
Tier 1
Denso Corp
- Denso Corp. is the largest automotive supplier in Asia. In 2019, it was ranked the second-largest part supplier globally by revenue.
- The company maintains its position as the market leader in the region. In 2019, the company generated 65% of its total revenue, about $27 billion, in Asia.
Aisin Seiki
- Aisin Seiki is the second-largest primary supplier to automotive OEMs in Asia with 71% of its revenue, about $23.7 billion, coming from Asia.
- Although Aisin Seiki is a market leader in Asia, its penetration in other regional markets is low, with the EU accounting for only 10% of its annual sales.
Hyundai Mobis
- Hyundai Mobis is the seventh-largest part supplier globally and the third in Asia. In 2019, Asia accounted for 65%, about $17 billion, of its global revenue.
- The organization is a prominent force in South Korea where it is headquartered, while it has a lower presence in other regions.
Tier 2
- Yazaki Corp is a top tier 2 supplier in Asia. The company generated $17.6 billion in 2020, of which $9.3 billion was generated from its operations in Asia alone.
- Beijing Hainachuan Automotive Parts (BHAP) is a tier 2 supplier that operates in Asia, Europe, and North America. In 2019, its total revenue was $4,045,000,000, with 70% of this figure earned in Asia.
Employee Count
- Denso — 168,390 employees globally.
- Aisin Seiki — 118,359 employees globally.
- Hyundai Mobis — 35,087 employees globally.
- Yazaki Corp — 306,118 employees as of 2018.
- BHAP — 27,000 employees globally.
Labor Right Issues
Labor rights violations have been reduced to a significant degree in the Asian automotive supply chain. None of the top tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers previously identified have been directly involved in labor rights violations in the past four years. Below are examples of recent labor rights violations in the Asian automotive industry:
- In 2017, while campaigning for equal pay, several employees at Changchun FAW-Volkswagen in Northeast China were arrested by the police. The arrested employees also wrote a public letter demanding that the organization take responsibility for the unlawful arrests and for labor rights abuses.
- After the release of the arrested workers, Volkswagen China agreed to look into the plight of its over 3,000 subcontracted agency workers.
- Hyundai Motors has had a long history of labor disputes since the inception of its workers' union in 1987, with worker strikes occuring almost every year. The last dispute organized by the company's South Korean workers in 2018 pushed Hyundai to shut down its factory and halt production temporarily, resulting in a loss of $37 billion. Since 2019, Hyundai has made sure to avert strike actions by its workers.
- Earlier this year, Hyundai's South Korean workers made new demands which the organization failed to initially satisfy. However, Hyundai reached an agreement with its workers' union and averted the strike before the planned walk-out was executed.
- In 2017, workers at the Maruti Suzuki factory in India embarked on protests to prompt the organization to address the condition of contract employees. The protests became violent and 148 workers were arrested and imprisoned, while others were severely injured. A total of 117 of them were eventually released while 13 others were sentenced to life for the murder of one manager who died in a factory that had been set ablaze.
APPAREL
Number of Suppliers
- There are currently no publicly available reports on the number of tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers that serve the Asian apparel industry. Also, lists containing the names of the top tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers for the Asian apparel industry are not currently available in the public domain.
- Supply chain traceability is still rather limited in the apparel industry. At the moment, only a few organizations disclose their tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers. In 2020, only 36% of the top 250 apparel brands shared the names and employee sizes of their tier 1 suppliers. Also, just 20% of the top global manufacturers shared details about their tier 2 suppliers.
- Despite a lack of actual data on the number of tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers in the Asian apparel supply chain, the region is often described as the "garment factory of the world." According to a study by the International Labour Organization (ILO), Asia is responsible for about 63.7 % of global apparel exports.
- In 2019, over 43 million workers were employed in the Asian apparel industry. The majority of apparel suppliers in the region are small to mid-sized businesses, which often operate small locally-owned production units.
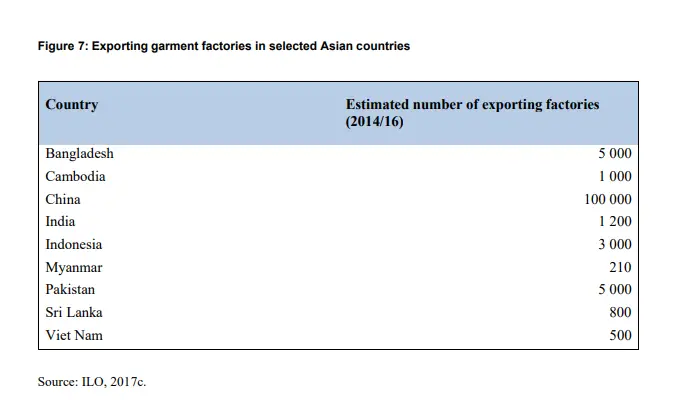
- China is currently the largest apparel-producing country in the region and the world. There are over 100,000 supplier factories in the country.
- Bangladesh and Pakistan both operate over 5,000 apparel exporting factories each. Suppliers in Vietnam operate about 2,500 factories, and Indonesian suppliers operate about 3,000 factories. Cambodia, India, Sri Lanka operate about 1,000 exporting factories each.
Main Suppliers
To identify notable suppliers that serve the Asian apparel industry, the research team reviewed several supplier lists of major clothing brands and identified tier-1 and tier-2 suppliers that possess significant employee count. Below are examples of notable tier-1 suppliers that focus on the Asian apparel market and their employee count:
Tier 1:
- Golden Star Co., Ltd
- Karooni Knit Composite Ltd.
- Location: Bangladesh
- Number of Employees: 7,838
- Interloop Limited (Hd-Ii)
Tier 2
Below are examples of notable tier 2 suppliers that focus on the Asian apparel market and their employee count:
- NZ Fabrics Ltd
- Location = Bangladesh
- Number of employees = 7,500
- Divine Fabrics LTD
- Location = Bangladesh
- Number of employees = 7,500
- Style Textile (Pvt.) Limited (Manga)
Labor Right Issues
Limited information exists on identified suppliers. None of the companies identified above have been involved in public labor disputes in recent years. Due to the unavailability of issues specific to the identified suppliers, a broader overview of major labor issues affecting the supply chain in the Asian apparel market has been provided below:
- The US has banned all cotton imports from China's Xinjiang region based on allegations of human rights violations and the use of forced labor. A publication released in 2020 revealed that China was using minorities for forced labor on cotton farms.
- The community most affected is the Uighurs, a predominantly Muslim minority group. China has continued to retaliate as clothing brands in the country start to face regulatory sanctions.
- Poor labor conditions have been a major problem in the textile and apparel industry. Many factories fail to provide a conducive work environment for their employees, thereby exposing them to hazards and death.
- In April 2013, a building in Dhaka, Bangladesh housing five garment factories collapsed, killing over a thousand people. Several years on, garment factory employees still work under extreme conditions while the factory owners put up a charade for the world.
- There have been widespread labor rights violations in Asia hinged on the COVID-19 pandemic. According to a recent report by the Business and Human Rights Resource Centre, several factories hid under the guise of COVID-19 to target and dismiss union members in their workforce who have protested against extremely low wages and exploitation.
- About 16 million apparel factory workers across Asia have lost their jobs since the pandemic began. There have also been reports of intimidation, harassment, and dismissal of union leaders. In 2020, Oxfam reported that 1,200 workers were dismissed by a major supplier in India "amid allegations of worker intimidation and union-busting."
CONSUMER ELECTRONICS
Number of Suppliers
- Information on the number of tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers in the Asian consumer electronics supply chain is not available in the public domain. There are also no independent estimates on the number of suppliers from third parties. However, the Asia-Pacific region is the largest producer of consumer electronics globally.
- According to a study by Manufacturing Market Insider, the APAC region accounted for 81.9% of the top 50 EMS revenue in 2020. China alone employs about 150 million workers in its consumer electronics industry. Southeast Asian countries together employ over 2.4 million workers.
Main Suppliers
Consumer electronics suppliers are often referred to as electronics manufacturing services (EMS). The suppliers are primarily grouped into tiers based on their size, such as the total amount of revenue they generate per annum. Tier 1 rank is for companies that generate over $5 billion per annum, while the tier 2 rank is for companies that generate between $500 million to $5 billion per annum.
- HonHai Precision is the number one EMS in Asia. It also has the highest market share globally and generates revenue totaling $181.893 billion annually.
- Pegatron is the second-largest supplier in the region and also second to HonHai Precision globally, with revenue totaling $47.504 billion.
- Wistron is the third-largest supplier in the region and also the third-largest globally, behind HonHai Precision and Pegatron. The company generated revenue totaling $27.594 billion in 2020.
Tier 2
- Kaga Electronics — 422,365 million yen ($3,8 billion)
- VTech Communications Ltd — $2.3 billion.
Employee Count
- HonHai Precision — 1,290,000
- Pegatron — 169,083
- Wistron — 82,955
- Kaga Electronics — 7,826
- VTech Communications Ltd — 25,000
Labor Right Issues
- In 2019, Foxconn together with its primary client, Apple were accused of breaking China's labor laws. The publication explained that the Foxconn factory had hired too many temporary workers, making up about 50% of its total workforce. This percentage is 5 times more than the 10% stipulated by the Chinese government.
- Both parties denied almost all accusations leveled against them, however, they agreed to over-staffing temporary workers. Apple released a statement announcing that all workers would be compensated as necessary.
- In 2020, Apple cut ties with Pegatron over allegations of child labor abuse. Pegatron, a Taiwanese manufacturer, misclassified student workers and made them work overtime and overnight. Apple made it clear that this practice violated its supplier code of conduct.
- Apple also alleged that Pegatron went to great lengths including forgery in an attempt to cover up its misdeeds. Pegatron, however, has promised to adhere to the rules henceforth.
- Workers at the Wistron manufacturing plant in Karnataka, India protested and vandalized properties belonging to the company. Investigations revealed that the company had breached Apple's supplier code of conduct and this had resulted in payment lapses and delayed wages for employees.
- According to the Department of Factories, Boilers, Industrial Safety, and Health, Wistron had also failed to hire human resource professionals who are capable of handling its workforce. The company incurred damages worth millions of dollars and had to shut down the factory and cease operations.
RESEARCH STRATEGY
This research was completed using independent survey studies, news articles, academic publications, and other reputable sources of information available in the public domain, such as government and corporate websites. In several cases, we used outdated sources due to the absence of more time-relevant information. The dated reports used in completing this research contained the few available insights in the public domain.