Part
01
of one
Part
01
ESG Leadership
Key Takeaways
- ESG leadership can be integrated into corporate and investment strategies through evaluating the corporate vision for sustainability, articulating the value creation of ESG initiatives, making ESG initiatives core of corporate strategy, focusing on select ESG initiatives, and seeking top management’s buy-in.
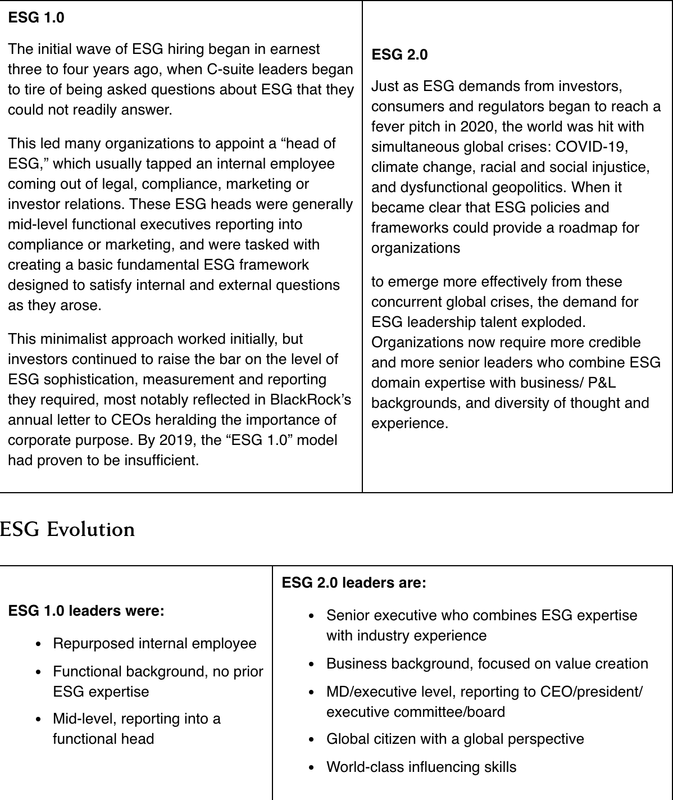
- The next-generation of ESG leaders will look different from ESG 1.0 predecessors since the scope of the role has grown and requires more senior and agile executives to be considered credible “ESG 2.0” leaders.
- The ESG 2.0 leaders are Senior Executives who combine ESG expertise with industry experience, have a business background and are focused on value creation, report to the CEO/President/Executive Committee/Board, and are global citizens with a global perspective, and world-class influencing skills. predominantly female who are hired from outside the corporation and bring cross-functional business expertise to the role.
- Boards, management and functions responsible for ESG initiatives should have sufficient ESG knowledge to oversee, manage and evaluate ESG strategies and performance.
- A company can incorporate sustainability values in the culture of a company through creating a purposeful culture, articulating the value creation, integrating ESG into the business , effectively communicating with stakeholders, and developing capacity on ESG.
Introduction
This report presents insights on integrating ESG leadership into corporate and investment strategies and incorporating sustainability values into the culture of a company. This includes insights into the next generation of ESG leaders (C-level, execs, shareholders, boards), the importance of incorporating ESG as part of an investment strategy, and the importance of ESG in the culture of a company. Below are the detailed findings and further details on the research process can be found in the research strategy at the end of this report.
Integrating ESG leadership into Corporate and Investment Strategies
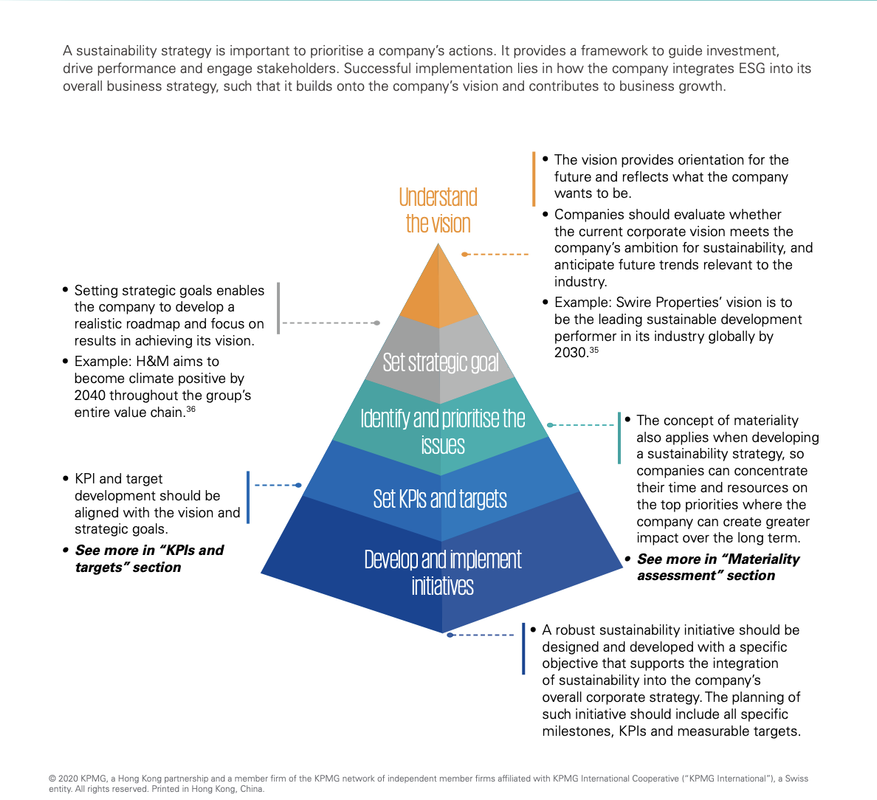
- The vision provides orientation for the future and direction for the corporation.
- Leadership evaluates whether the corporate vision meets the corporation's ambition for sustainability and anticipates future trends.
- Leadership sets ESG goals that enable the corporation to develop a realistic road map and focus on achieving its vision.
Understand the Vision
Set Strategic Goals
Prioritize ESG Initiatives
- Leadership articulates the value creation of ESG initiatives relevant to the organization. About 70% of business leaders acknowledged that ESG is essential as a value creation.
- Leading CEOs make ESG initiatives core of the corporate strategy by focusing on select initiatives that have an impact on society and competitive position.
- Leadership selects ESG initiatives that are most important to the corporation’s industry, aligned with the corporation’s purpose, and can have an impact on its competitive position with customers, employees, investors, and lenders.
- Develop KPIs to measure impact, align incentives to ESG goals, manage the underlying data with technology, and develop processes to monitor progress.
- Examine the attainability of the targets which should be weighed against the corporation’s vision and ESG goals.
- Useful and comprehensible ESG reporting metrics are critical to communicating the sustainable outcome of an investment portfolio. Companies should focus on progress toward its ESG goals.
- Seek top management’s buy-in to secure the resources necessary for target setting and implementation.
- Deep fundamental analysis combined with proprietary data, a research budget, and cutting-edge data science tools provide a holistic assessment of sustainability and better-informed investment decisions.
Set KPIs, Targets, and Metrics for ESG Initiatives
- Robust ESG initiatives should be designed and developed with specific objectives that support the integration of sustainability into the corporate strategy.
- The ESG initiative should include all specific milestones, KPIs and measurable targets. The implementation and performance should be closely monitored and effective communication with key stakeholders about the progress is essential.
- The next-generation of ESG leaders will look different from ESG 1.0 predecessors since the scope of the role has grown and requires more senior and agile executives to be considered credible “ESG 2.0” leaders.
- The ESG 2.0 leaders are predominantly female who are hired from outside the corporation and bring cross-functional business expertise to the role.
- They are Senior Executives who combine ESG expertise with industry experience, have a business background and are focused on value creation, report to the CEO/President/Executive Committee/Board, and are global citizens with a global perspective, and world-class influencing skills.
- The ESG 2.0 leaders create a best-in-class enterprise-wide ESG policy and framework, integrates ESG policy across the organization, serves as the “face of the franchise” both internally and externally, and engages with external partners to help them create sustainable business strategies for their own corporations.
- In hiring this talent, it is integral that ESG is perceived as a core component of the business strategy, ESG is a priority for the C-suite and board, and the Head of ESG reports directly to the C-suite.
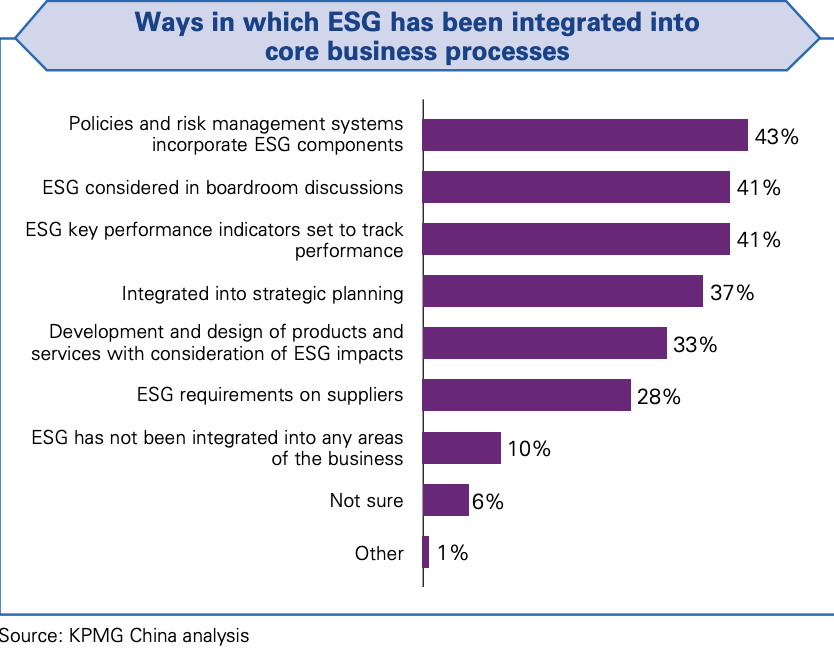
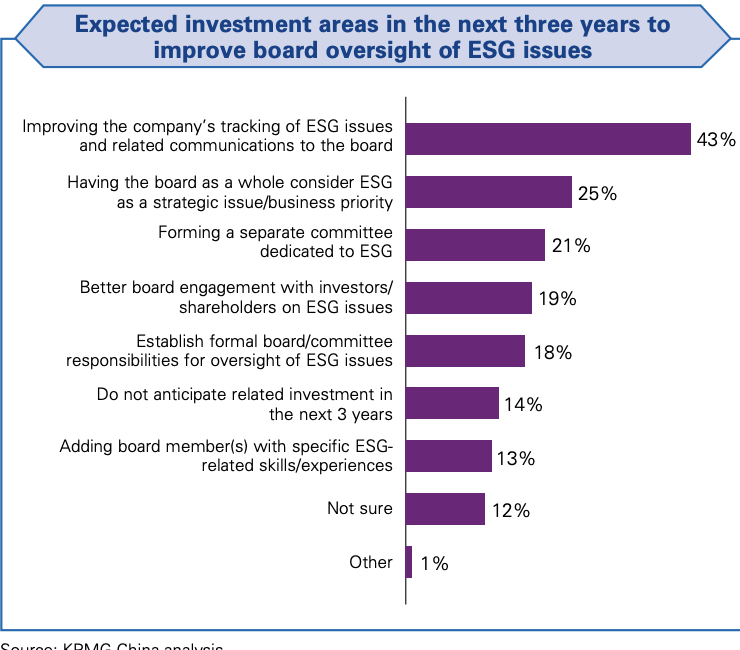
- Boards play significant roles in driving corporations' ESG development. Boards, management and functions responsible for ESG initiatives should have sufficient ESG knowledge to oversee, manage and evaluate ESG strategies and performance.
Develop and Implement ESG Initiatives
The Next Generation of ESG leaders (C-level, execs, shareholders, boards)
Incorporating Sustainability Values into the Culture of a Company
Develop a Purposeful Culture for ESG
- Create a purposeful culture that will drive ESG initiatives and align ESG mission, vision, and principles within a corporation.
- Employees should feel a strong sense of purpose, contribute to the ESG mission and vision and have a positive impact on customers and the community.
- Identification, communication, and management of ESG challenges and opportunities will be more effective since employees have a greater commitment.
- A top-down approach of ESG integration in a corporation. The culture should be exemplified at the top and cascaded through all levels of the corporation and to key stakeholders including investors, suppliers and local communities.
- The management should drive the culture while the board should monitor and assess the culture.
- ESG initiatives should be clearly articulated, and CEOs must rally support around the initiatives and focus on long-term potential for innovation and disruption.
- Leadership should articulate the value creation of the ESG initiatives and the link between sustainability and long-term value creation should be communicated within the organization.
- Corporations that adopt a long-term approach will make more investments which will help increase productivity and competitiveness in the future. On the other hand, adverse impacts of short-term approach include undermining future innovation, hindering product enhancement, and hindering research and development.
- ESG initiatives should create value that is measurable through hard metrics that feed into the business model.
Articulate the Value Creation of ESG
- Leadership should integrate ESG into the business through building awareness, strategic planning, policy making, risk management, metric setting, metric tracking, and communication.
- The integration should be supported by effective board oversight that will focus on strategically significant ESG issues and monitor ESG performance.
- The board should monitor ESG performance against the corporation's goals and address ESG issues on a regular basis, and communicate to the board the ESG issues addressed in the corporation's risk management process.
- A diverse board comprising members of different backgrounds, experience and strong ESG expertise enables effectiveness oversight of ESG issues.
- Effective communication with internal and external stakeholders is integral in conveying long-term value creation and building a mutual understanding on ESG strategy and direction.
- Corporations should establish effective, open and regular channels of communication to internal and external stakeholders.
- Corporations should communicate to stakeholders about the long-term goals, vision and strategies, make a business case for long-term investment, communicate reasons for capital allocation priorities, and communicate the real value of ESG reporting.
- Develop capacity on ESG for both implementors of ESG strategies and senior management including the board and the C-suite.
- Global sustainable investment was about $30 trillion in 2019 up 68% since 2014. The huge global investment in ESG suggests that it is not a fad or a new buzz but is mainstream. In addition, research finds that corporations that are keen on ESG have a better level of business performance and value creation for shareholders.
- ESG has moved from being a functional requirement to a commercial imperative with financial benefits of incorporating sustainability into corporate and investment strategies.
- Investors and leaders realized that ESG integration can safeguard a company’s long-term success. In an EY CEO Survey 2022, 82% of United States CEOs reported that ESG investment is a key strategic value driver.
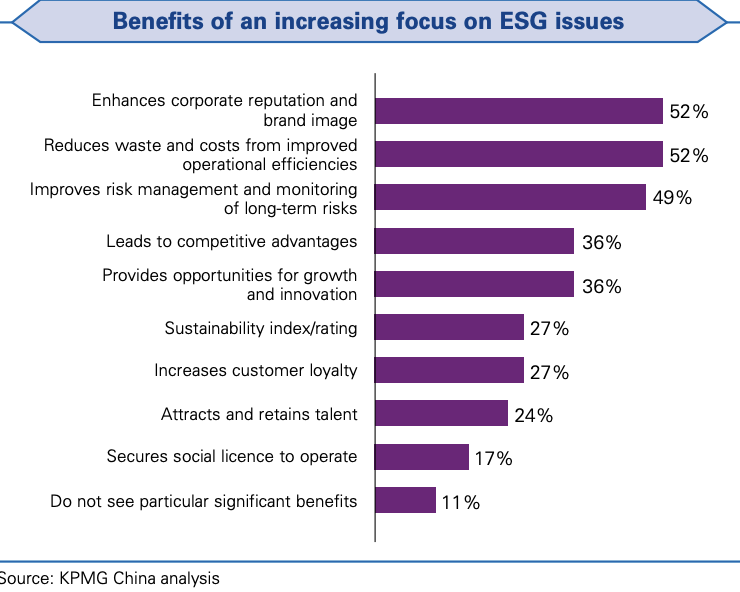
- The main benefits of ESG incorporation are enhanced corporation reputation, improved operational efficiency and better risk management. An ESG strategy can enhance deeper customer relationships and loyalty, ability to attract and retain talent, ability to attract capital, resilience, and reduce regulatory risk.
- Long-term value created by ESG include driving growth, innovation and competitive advantage. “Leadership teams that focus on an ESG approach that is directly tied to their corporate strategy can make their companies stand out from the competition. Those that do not will fall behind when confronted with regulatory, customer and investor pressure.” Corporations that are keen on ESG have a higher value than their competitors.
Integrate ESG into the Business
Effectively Communicate with Stakeholders
Build Capacity on ESG Issues
Importance of ESG and its Financial Sense in an Investment Strategy
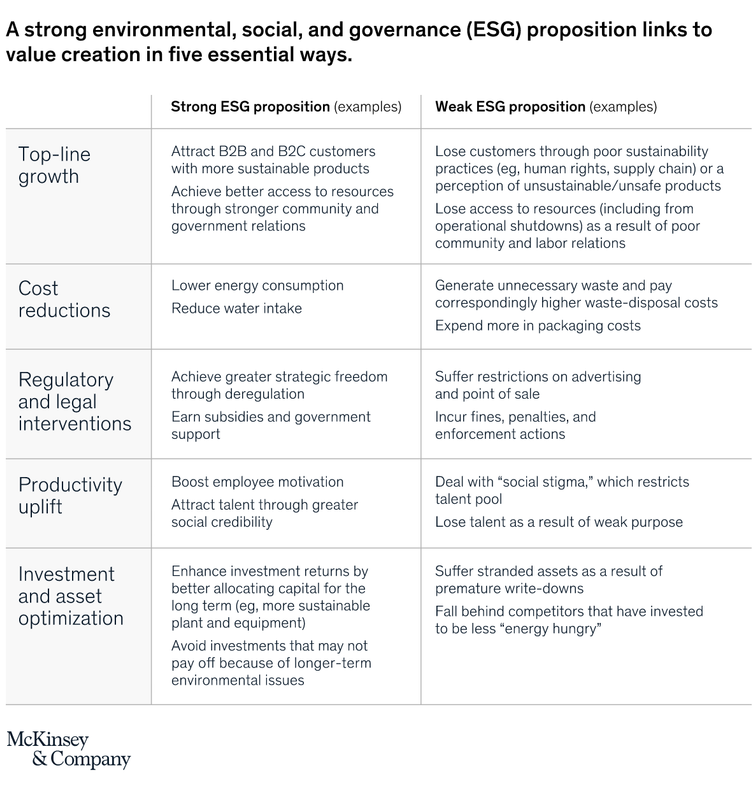
- The payoffs for ESG include top-line growth, minimizes costs, reduces regulatory and legal interventions, improves employee productivity, and optimizes investment and capital expenditures.
- ESG integration helps corporations tap new markets, expand existing markets, drive consumer preference, reduce operating expenses, reduce risk of adverse government action, attract government support, attract and retain quality employees, enhance job satisfaction, increase productivity, and enhance investment returns.
- Examples of corporations that have benefited from ESG: Finland’s Neste which generates over two-thirds of its returns from renewable fuels and sustainability-related products, and 3M which saved $2.2 billion since 1975 by preventing pollution through “reformulating products, improving manufacturing processes, redesigning equipment, and recycling and reusing waste from production.”
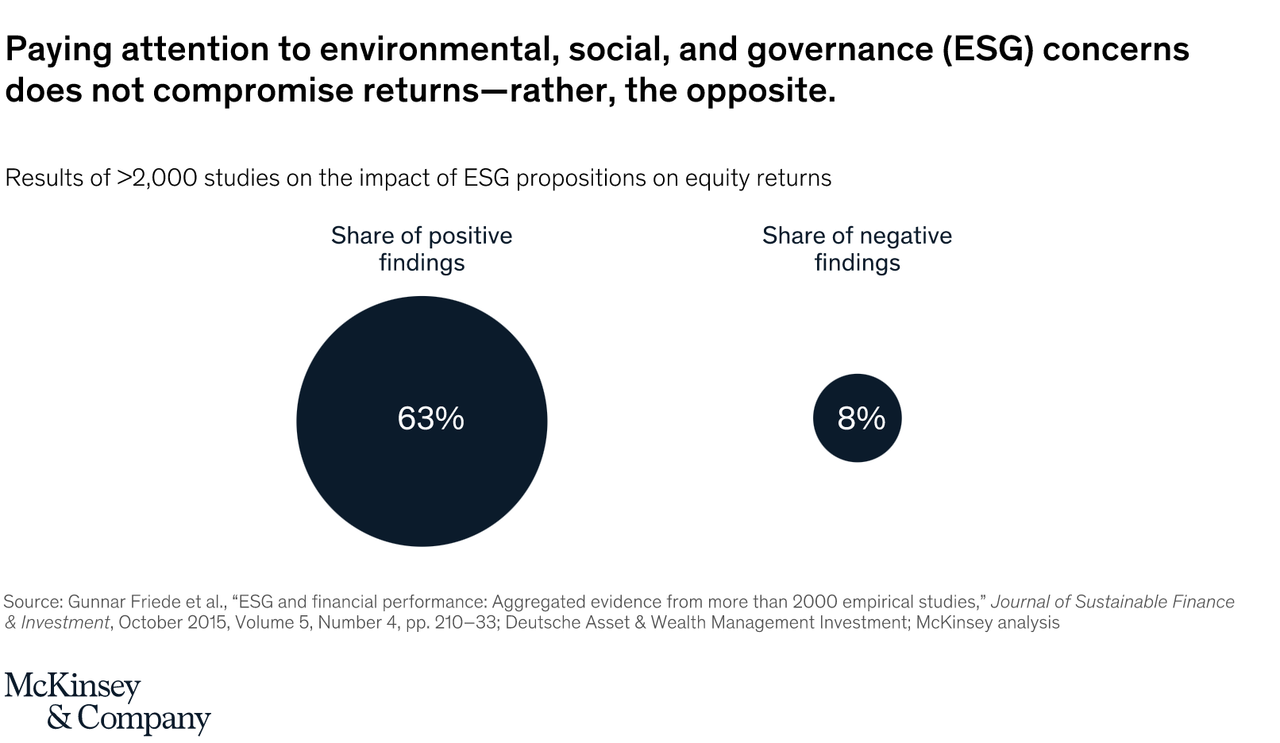
- Integrating ESG factors into investment leads to superior risk-adjusted returns and lower volatility. Asset owners adopted sustainable investing and advocate for long term, sustainable, and risk-adjusted returns. They screen out firms or industries from the investment portfolio if their practices counter the corporation's values.
- Sustainable investing should allow investors to capitalize on some long-term trends and themes of the future.
Strategy
For this research on Responsible ESG Leadership, we leveraged the most reputable sources of information that were available in the public domain including McKinsey, CFA Institute, EY, KPMG, J.P. Morgan, Morgan Stanley, and Harvard University.