Part
01
of one
Part
01
AI-Coaching and AI-Therapy
Key Takeaways
- Leaders in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Conversational AI Platforms in 2022 were Kore.ai, Amelia, IBM, Omilia, Cognigy, and OneReach.ai.
- GPT-3 is the newest iteration of OpenAI's language model in which GPT-3 comprises more than 175 billion parameters, compared to 1.5 billion with GPT-2.
- The International Coaching Federation in its ICF Global Coaching Study for 2020 estimates that there were 71,000 coach practitioners in 2019, a 33% increase on the 2015 totals. The average annual income globally was $47,100 and the market size was estimated at $2.849 billion, a 21% increase from 2015.
- More than 50 companies are developing AI processors including Amazon, Facebook, Google, and Qualcomm.
Introduction
This research brief provides concept overviews of conversational AI, the current state for AI-based coaching and AI-based therapy, and best practices for the development of sophisticated AI chatbots. Details of the research strategies employed for each section is provided in the Research Strategy Section below. Please note that in some instances, sources that were slightly older than Wonder's usual two-year limit were used.
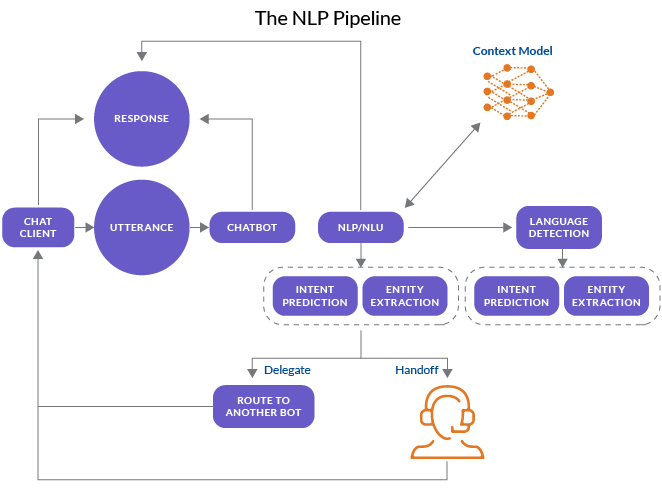
Conversational AI — Concept Overview
Conversational AI Definition
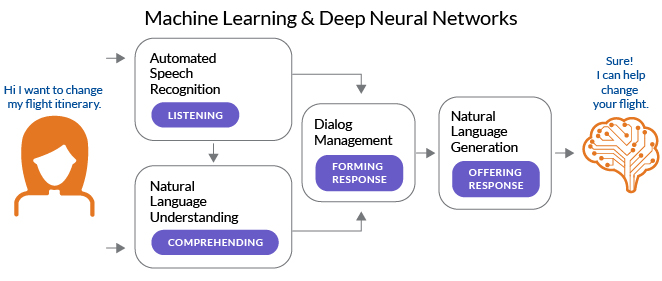
- According to IBM, conversational AI are technologies that can talk to users by imitating human speech. This is made possible from the use of data, machine learning, and natural language processing.
- Machine learning (ML) refers to the algorithms, data sets, and features that improve through pattern recognition gleaned from experience. Predictions are made, and produce better results as the platform improves.
- Natural language processing (NLP) refers to the analysis of language using machine learning. The four steps of NLP are input generation, input analysis, output generation, and reinforcement learning.
What is the Best Conversational AI System?
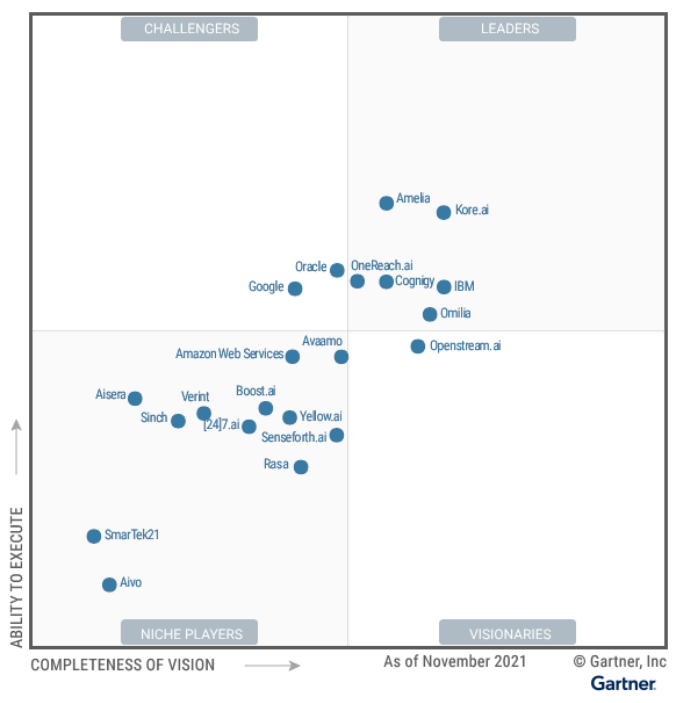
- On 24 January 2022, Gartner published its Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Conversational AI Platforms.
- Leaders in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Conversational AI Platforms in 2022 were Kore.ai, Amelia, IBM, Omilia, Cognigy, and OneReach.ai.
- Challengers were listed as Oracle and Google.
- Openstream.ai was named as the sole visionary for 2022.
- Niche players were identified as Avaamo, Amazon Web Services, Senseforth.ai, Yellow.ai, Boost.ai, [24]7.ai, Verint, Rasa, Sinch, Aisera, SmarTek21, and Aivo.
- Gartner's reasons for the selection of each company in all four categories can be sourced in this article from CXToday dated 31 January 2022.
Cutting-Edge Conversational AI Technology — Companies
- Google, and OpenAI, are two companies providing cutting edge technologies for conversational AI. Google was mentioned in an article in MIT Technology Review, and OpenAI in an article in AI Express.
Google LaMDA
- Google CEO Sundar Pichai launched the company's conversational AI tool LaMDA on 18 May 2021.
- LaMDA is considered cutting edge because of the wide-ranging topic on which it can converse.
- LaMDA, Language Model for Dialogue Applications, is built on the Transformer neural network, also a Google property. Trained on dialogue, LaMDA has the ability to understand nuance in open-ended conversations.
- In tests conducted at Google, LaMDA outperformed the pre-trained model in sensibleness, safety, specificity, groundedness, interestingness, and informativeness.
OpenAI
- OpenAI is involved in the research and development of AI technologies.
- In May 2020, the company released its paper describing how GPT-3, the newest version of its "state-of-the-art language model" was developed.
- GPT-3 is the newest iteration of OpenAI's language model in which GPT-3 comprises more than 175 billion parameters, compared to 1.5 billion with GPT-2.
- GPT-3 is considered cutting edge because of its ability to produce short paragraphs and sentences that are very close, if not indistinguishable to that written by humans.
- Companies using GPT-3 are IBM, Salesforce, Cisco, and Intel.
How are the algorithms trained and improved?
- Conversational AI can be trained and improved either through progressive reinforcement learning or by conversation design.
Reinforcement Learning
- The training of machine learning models to make decisions in sequence is termed reinforcement learning. In a game-like environment, trial and error is deployed to iterate to a solution, with rewards and penalties acting as the carrots and sticks.
- Challenges associated with reinforcement learning are preparing the simulation environment, being easily able to tweak and scale the controlling agent for the neural network, attaining local optimum (the task is performed as is not in the required way), and prize optimization without performance
Conversational Design
- Design languages that are based on human conversation are termed conversation design. Elements of conversation design can be drawn from audio design, interface design, interaction design, motion design, visual design, and UX writing.
- Conversation design employs the use of personas to develop the conversation. These can be system personas or user personas. It is differentiated from chat bots by its ability to synthesize advanced analytics and integration, contextual awareness, exception/escalation management, intent management, language processing, and response generation.
- The technologies underlying conversational design are NLP, sentiment analysis, deep learning, and intent prediction.
Conversational AI Chatbot-Human Parity & its Roadblocks
- Writing in an article in VentureBeat's Data Decision Makers series dated 23 February 2022, Jiang Chang, vice-president of machine learning at Moveworks, noted that conversational AI chatbots noted that the challenges are "daunting" when it comes to chat bots participate in a conversation requiring context, interpretation, and decisions on how to respond.
- These challenges are listed below.
- Latency — Improving conversational AI in all its forms to handle complex conversations, whether in live environments or the more sedate academic environment, means increasing the complexity of the program and the underlying machine learning processes.
- Dependency Hell — High latency is dependent on applying the shortest sequence to achieve the critical path from input to the bot's response. Determining the critical path for connected software architecture in a machine learning environment means solving for probability distributions, i.e. making changes to a model with the attendant impact to the wider network unclear. When this process is mastered for machine learning, only then will fully real-time conversational AI become a reality, notes Mr. Chang.
AI-Based Coaching and AI-Based Therapy — Concept Overview
AI-Based Coaching — Strengths
- Strengths of AI-based coaching are listed below.
- Price — AI-based coaching is cheaper than executive coaches.
- Accessibility- As a lower priced product coaching is accessible to a wider audience in the company.
- Market Opportunities — The International Coaching Federation in its ICF Global Coaching Study for 2020 estimates that there were 71,000 coach practitioners in 2019, a 33% increase on the 2015 totals. The average annual income globally was $47,100 and the market size was estimated at $2.849 billion, a 21% increase from 2015.
- Collaboration — AI-based coaching can supplement and complement the work of a human coach from the provision of real-time data, suggest topics to be pursued, act as a quality check and sounding board for the human coach, and enhances the session review process.
- Data — In the workplace, activity data can be sourced from the employee's interactions with business systems and be used to identify potential issues as they are developing. Managers can then step in with corrective measures to address the employee behavior before it negatively impacts work.
- Benefits of AI-coaching for the company include ease of set-up and use, outsourced administration, increased participation rates and user satisfaction than in voluntary programs, positive behavior change, increased employee engagement and retention, culture change and better performance outcomes.
- For employees and managers, the benefits of AI-based coaching are development that occurs in-the-flow, improved digital communications and collaboration, improved emotional intelligence and self awareness, and increased trust in the company.
AI-Based Coaching — Weaknesses
- Weaknesses of AI-Based Coaching are listed below.
- Mechanism — Human coaching eventually evolves from models and processes towards in the moment responses. AI-based coaching may be susceptible to mechanistic conversations as a result of information overload.
- Gender Bias — A problem rooted in the development of training data for AI, gender (and other) biases impact on AI-based coaching when decision-making is predicated on historic patterns, rather than the exercise of judgment to evaluate the present situation.
AI-Based Therapy — Strengths
- Strengths of AI-based therapy are listed below.
- Quality Control — AI can be deployed in clinics to maintain and monitor quality control.
- Improved Diagnostics — AI is better suited for sifting through massive amounts of data to assist physicians with personalizing treatments.
- Patient to Physician Matching — Insights derived from data can assist with matching clients to therapists.
- Patient Monitoring — AI assists physicians with patient monitoring and can identify when treatment, or physicians, needs to be changed.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Validation — With prescriptions for mental health increasing, AI provided the evidence on which CBT is applied.
- Affordability — Therapeutic help can be accessed anywhere at little to no cost.
- Accessibility — Circumvents staff shortages since AI chat bots and platforms are location agnostic.
- Efficiency — AI-based therapy has been more accurate at making assumptions regarding the veracity of suicide notes and forecasting at-risk teams that would eventually develop psychosis.
- Collaboration — AI can provide evidence on which physicians can base decisions.
- Privacy — AI-based therapy may encourage more sharing due to its privacy features.
AI-Based Therapy — Weaknesses
- Weaknesses of AI-based therapy are listed below:
- Training sets — The training sets on which AI is trained may contain biases and the characteristics for the data may constrain creative, emphatic, and rational responses.
- Lack of regulation.
- Patient Data Security.
AI-Based Therapy and Human Parity
- Once source was found that directly addressed AI and human parity for therapeutic treatments. Unfortunately this source is paywalled. Details on the source are provided below.
- On21 March 2021, the Wall Street Journal published an article titled "Can Artificial Intelligence Replace Human Therapists?" In the article three experts discussed the pros and cons of relying on mental health algorithms. This source is paywalled.
Hardware and Software Breakthroughs
- Publicly available data on hardware releases specific to AI-based coaching and therapy is not available. In its place we have provided hardware advances that are believed to be able to further advance the AI revolution that have the potential to impact on AI-based coaching and therapy.
- On 10 March 2022, Semiconductor Engineering published an article in which seven hardware advances were identified to further the AI Revolution. These are listed below:
- Specialized Processing — More than 50 companies are developing AI processors including Amazon, Facebook, Google, and Qualcomm.
- Near Data Processing — Aimed at reducing the more than 60% of energy that is used by computers in the digital commute between memory, processing units, and storage.
- Non-CMOS Processors — The production of cheap neural networks to be used in integratable, low-cost processing.
- Event-based/Threshold Processing — This refers to data updates that occur only when changes occur, thereby reducing the total amount of data captured. An example would be capturing changes in the movement of a body only as opposed to also capturing data on static backgrounds.
- Neuromorphic Processors — The design of artificial spiking neural networks based on the architecture of the human brain.
- Extreme Ambient Cooling — Examples of this include data centers implanted in abandoned mines, city harbors, and bomb shelters.
- Zero Compute Architectures — Systems that are able to perform intensive tasks that have already been performed once.
- For AI-based coaching Josh Bersin identified two broad categories for digital disruptions in July 2021. These are intelligent assessments (e.g., BetterUp's Whole Person Model) and algorithmic coaching (Cultivate). Algorithmic coaching is seen as the market to expect higher growth from.
- For AI-based therapy, a team from the University of Washington School of Medicine, the University of Southern California, and the University of Pennsylvania has developed an automated evaluation software to assist behavioral health trainees to counsel effectively and to maintain skill sets. Additional information can be sourced from this link.
Companies with Sophisticated Algorithms
AI-Based Coaching
- Cultivate — The Cultivate algorithm monitors online employee communications and interactions to identify behavioral trait and provide analytics, insights, and coaching. At SAP 83% of managers thought the tool improved performance, while 96% remain engaged with the tool and 86% engage with the monthly recommendations. This resulted in a 17% increased manager recognition of employee efforts.
- BetterUp — At BetterUp the Whole Person Model an intelligent assessment model employs AI to assess current performance, identify learning style and learn user preferences, suggest areas to improve, and match to coaches. At Google deployment of the BetterUp Whole Person Model results in a 29% increase for strategic planning, 37% increase in sphere of influence, 22% increase in work-life balance, and 16% increase in cognitive agility.
- Torch — The People Development Platform integrates coaching into learning paths with assessments, content, mentors, and peer groups. At Twitch key results include employees requesting coaching after the end of the initial engagement and a coach NPS score of 79.
AI-Based Therapy
- Ieso bills itself as the first company globally to address therapy language using machine learning. Mental illness is identified, treated, or prevented from the application of deep-learning capabilities delivered in concert with clinical and scientific experts. The company has partnered with Roche, University of Oxford, University of Cambridge, Tufts University and the Digital Therapeutics Alliance to deliver this service.
- Lyssn advances AI technology in behavioral health by applying machine learning, software engineering, speech signal processing, and user-centered design int eh development of mental health solutions that are cost-efficient and scalable. Current products in development include the CBTpro developed with the Behavioral Research in Technology and Engineering (BRiTE) Center at the University of Washington, and the ClientBot, a conversational AI tool for counseling skill development.
Best Practices — Building a Sophisticated Chatbot
Toptal for Top Engineers
- Toptal is a network of screened, freelance software developers. Freelancers on the platform are not only screened for their technical skills, but also for work attitude, energy, education, ethics, and proficiency in English. The company claims to only hire the top 3% of global freelance talent.
- Using Toptal to source the best freelance engineers was included as the best practice because of the wide range of top tier clients that has accessed the talent on the platform. Clients have included Bridgestone, Cleveland Cavaliers, Calm, Duolingo, Motorola, Shopify, Zendesk, Gucci, and Priceline.
- Toptal was also chosen because one of its talents was used by the University of Southern California to develop an online student wellness tool, Ask Ari. Ask Ari assists students with mental wellness issues with no judgment and with privacy. The tool is available to the University's more than 40,000 students.
- The Wall Street Journal noted that using Toptal "...allows corporations to quickly" build project teams, while Bloomberg Business notes that vetting at Toptal attains almost Ivy-League levels.
Developer and End-User Experience.
- Alan Nichol, co-founder and chief technical officer at Rasa, believes the end-user and developer experiences have to be improved for conversational AI to be accessible for everyone.
- Mr. Nichol's has identified five levels that are applicable to both developers and end-users along the path to conversational AI/AI chat bot to human parity.
- From the end-user perspective level progress takes place from the basic static web form (Level 1) to basic chatbots (Level 2), to contextual assistants (Level 3) to consultative assistants(Level 4) and finally to adaptive assistants (Level 5).
- From the developer perspective adding new functionality is easy at Level 1, at level 2 it becomes more difficult with an evolving assistant, at Level 3 developers come to terms with the fact that some messages cannot be classified as intents, at level 4 automation of the conversation driven-development (CDD) process begins, and at level 5 there is a fully automated CDD process.
Open Source vs Proprietary Frameworks
- Chatbots can be deployed using platforms with pre-built modalities, or by pursuing an independent build from scratch using tools such as Dialogflow from Google or Lex from Amazon, while open Sourcing provides a mid-point for implementation.
- With an open-source development, the chatbot has a steep learning curve, the communities are developer focused without a focus on design, and the total cost also has to account for training, servers, implementation, and hardware.
- Proprietary platforms, particularly those that are industry specific, can reduce production, training, and testing timelines. Popular platforms for open source chatbots are Microsoft Bot Framework, Rasa NLU, BotPress, AnaChat, and Botkit.
- Alan Nichols CTO at Rasa noted that open-source and enterprise are two sides of the coin. Further, open source is primarily targeted at developers, whereas enterprise has multi-disciplinary teams and presents a fuller option for the development process.
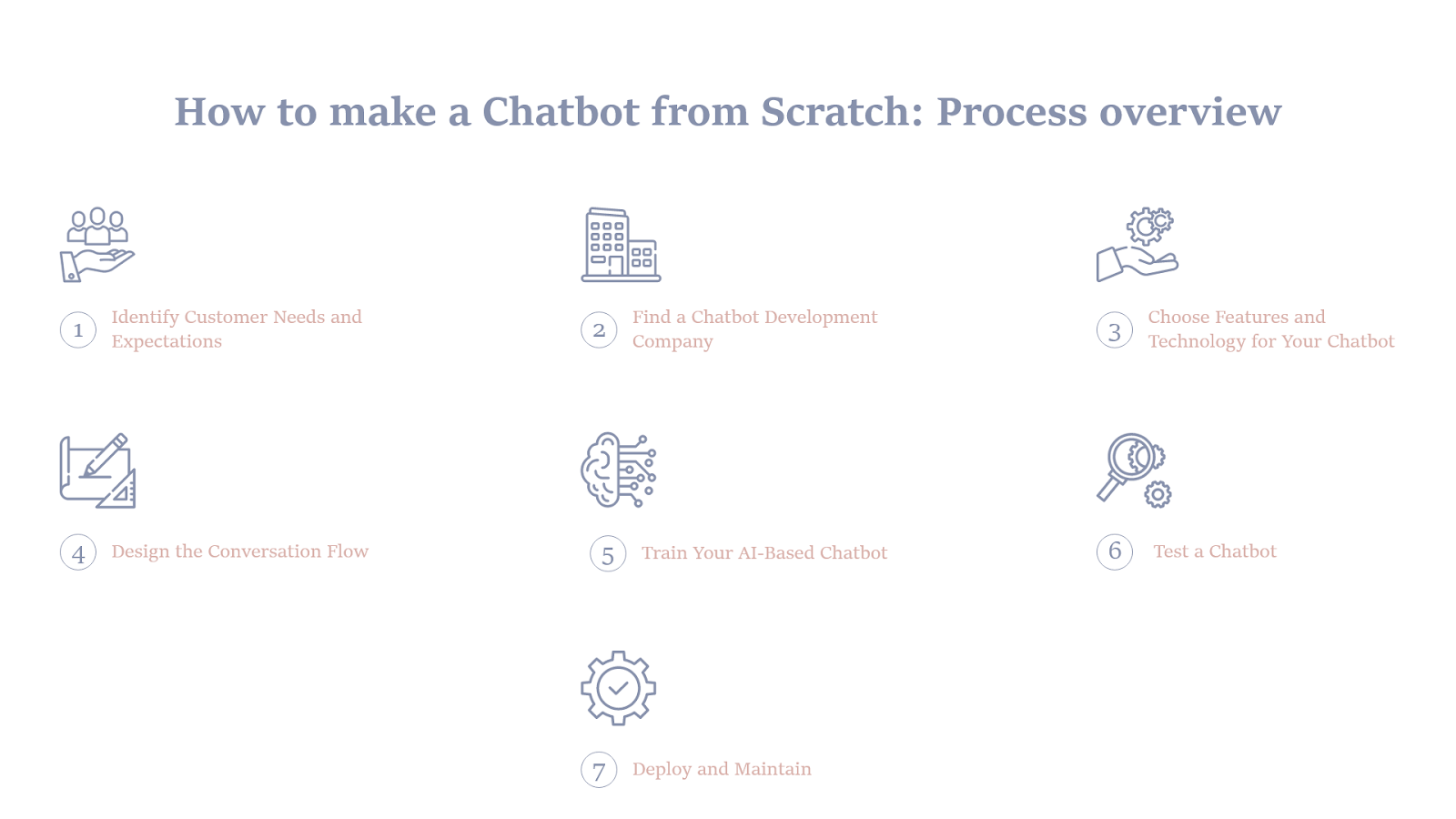
Focus on Process
- Defining the project begins with identification of the conversational scenarios that will be the foundation for the chatbot.
- Sourcing material from internal departments (such as Customer Service) creates a database that is relevant to the businesses' peculiar needs. It is also important to decide on integration for the chatbots.
- Additional key steps in the process are configuration of intents for the bots, personalization features to be incorporated, testing, incorporation of additional AI features to enrich the chatbot such as humor, language processing, information interpretation, user intent detection, and sensory perception, and post implementation enrichment of the chatbot.
- At Senseforth.ai non-coding environments are also discussed as an option for building bots for beginners or non-technical users and at Inbenta security and quality are also built into the design.
Focus on UX design
- UX design is not only important for brand identity but also to engender a great user experience.
- Designing AI chatbots for an optimal UX design comprises the following best practices:
- Providing an end-to-end user experience.
- Enabling smart suggestions with buttons or quick replies.
- Analyzing user behavior for prediction and preemption.
- Cross referencing.
- Add smart elements such as forms, calendars and maps.
- Keep responses concise.
- Match company branding.
- Manage specificity.
- Build in politeness.
- Balance playful and useful carefully.
- Additional design considerations impacting on the user experience and conversation design are the purpose of the chatbot, research, user goals, intents and entity identification, tone and voice, mapping conversational branches, and dialogue.
- Regarding the design of the conversation, best practices include the avoidance of "yes" and "no" responses from the chatbot, using contractions, forward movement with each response, including solutions with responses, adding links to explanatory content, providing buttons and links for clarity, and updating intent and entities to reflect dynamism in content.
- Interaction design best practices include setting expectations early, using common language, enabling flexibility in interactions, designing for trust, transparency, and explanation, enabling user control and feedback, and testing.
- Sajid Saiyed believes that voice-enabled chatbots should be learning language and human intents, not vice versa.
Research Strategy
For this research on AI-based coaching and AI-based Therapy, we leveraged the most reputable sources of information that were available in the public domain, including from IBM, Gartner, and MIT Technology Review.
For the section on conversational AI, the research strategy used was to consult the rating agencies (e.g., Gartner), service providers (e.g., OpenAI), and industry publications (e.g., MIT Technology Review).
For the section on AI-based coaching and AI-based therapy, the research strategy employed was to consult the science or data web pages for industry practitioners (e.g., Ieso), industry associations (e.g., International Coaching Federation), and industry publications (e.g., JoshBersin.com).
For the section on best practices in the development of sophisticated AI chatbots, the approach taken was to consult academic databases (e.g., uxpamagazine.org) and industry practitioners (e.g., Senseforge.ai).
In some instances, slightly dated resources were used to add robustness and/or corroboration to the findings, considering the highly specific nature of the topic and the limited availability of more recent reputable sources.